FIG. 2.
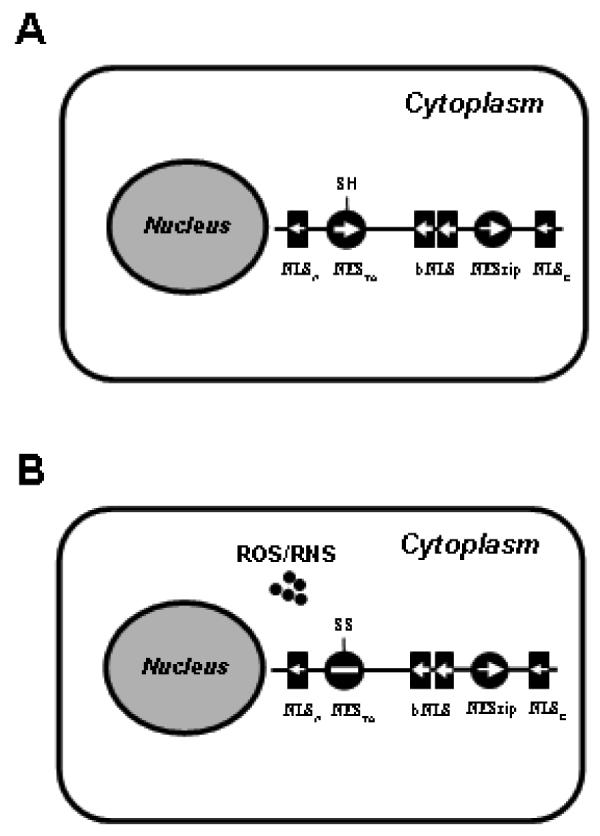
Nrf2 functions as a redox probe. The identified NES and NLS motifs of Nrf2 are symbolized by filled circles and boxes, respectively. Their driving forces are designated by the direction and size of the arrows. During the unstimulated condition (A), two NES motifs can counter balance the combined driving force of the bNLS, NLSN and NLSC motifs and sequester Nrf2 in the cytoplasm. When challenged by oxidative stress (B), the reactive cysteine in the NESTA can detect the presence of reactive oxygen species (ROS) or reactive nitrogen species (RNS) and disable the NESTA (plain line). As a result, the driving force of the bNLS, NLSN and NLSC motif prevails and causes Nrf2 nuclear translocation.
