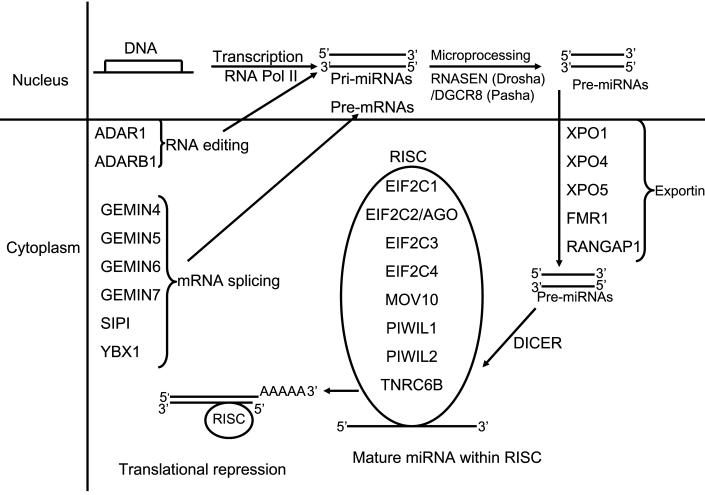
Figure 1.
Summary of miRNA processing machinery. In the nucleus miRNA are transcribed by RNA polymerase and are termed primary miRNAs (1°miRNAs). The dsRNA-specific ribonuclease RNASEN (Drosha) digests the 1°miRNAs in the nuclease to release hairpins, precursor miRNA (pre-miRNA) which are transported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm by exportins. Once in the cytoplasm, DICER cleaves the pre-miRNA approximately 19 bp from the Drosha cut site. The resulting double-stranded RNA has 1–4 nt 3′ overhangs at either end. Only one of the two strands is the mature miRNA. To control the translation of target mRNAs, the double-stranded RNA produced by DICER must strand separate, and the single-stranded mature miRNA must associate with the RISC. Post- transcriptional modifications such as splicing and editing play a part in miRNA processing.