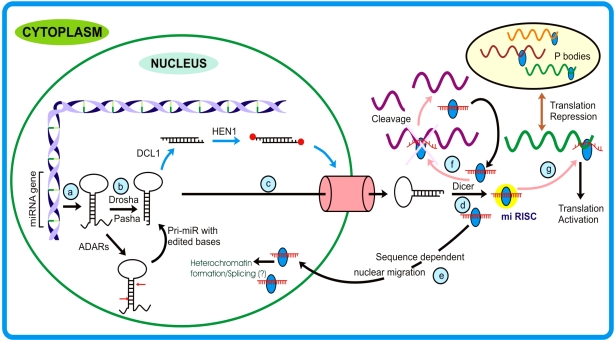
Figure 3.
MicroRNA pathway: (a) After being transcribed, the pri-miRNAs stem-loop structure is acted upon by (b) Drosha (that also confers to miRNA strand and target specificity) and generates pre-miRNA. Sometimes, these precursors are edited by Adenosine Deaminase Acting on RNA (ADARs) at specific positions (generally +4 and +44) changing adenine to inosine. In plants, the DCL1 generates miR duplex in the nucleus that is methylated at terminal bases by HEN1. (c) These are then transported to cytoplasm with the assistance of Exportin-5/ HASTY. From here (d) Dicer comes into play (in animals) and generates miRNA duplexes that will be incorporated into micro Ribo-Nucleo-Protein (mi-RNP) complex. After the removal of passenger strand mature miRNA then guides the functional protein complex to the targets. (e) In mammals, miRNAs bearing nuclear signal sequences can traffic back to the nucleus. Depending upon the proteins associated with miRNA leads to either (f) cleavage of target mRNA or modulate the translation turnover by (g) translation activation or repression of respective mRNAs. The repressed mRNAs are transferred to structures called P-bodies.