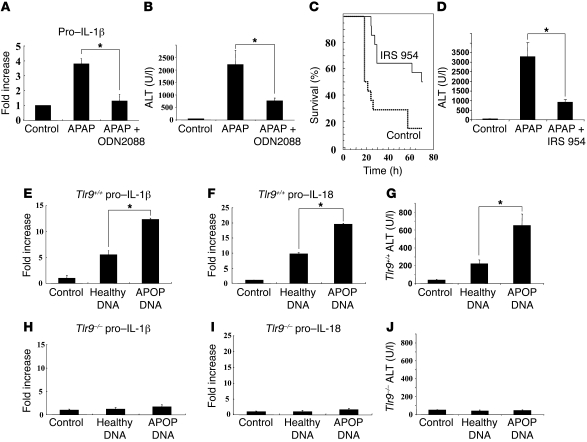
Figure 2. Reduction in liver injury by Tlr9 antagonist and induction of liver injury with apoptotic DNA.
(A and B) Treatment of Tlr9+/+ mice with the Tlr9 antagonist ODN2088 significantly reversed the APAP-induced rise in liver pro–IL-1β transcript and serum transaminase levels (*P < 0.01). (C and D) The Tlr7 and Tlr9 antagonist IRS 954 significantly decreased mortality from APAP over 72 hours and also reduced elevations in serum ALT at 12 hours after APAP (control: n = 14, IRS 954: n = 14, P < 0.006; *P < 0.01). (E–G) Direct administration of DNA from apoptotic hepatocytes into the blood supplying the liver resulted in an increase in hepatic transcripts of pro–IL-1β and pro–IL-18 and serum transaminases in Tlr9+/+ mice. Both serum transaminase and pro–IL-1β and pro–IL-18 transcript levels were lower after injection of DNA from healthy hepatocytes (*P < 0.01). (H–J) In control Tlr9–/– mice, there were no significant changes in serum transaminases and hepatic transcripts of IL-1β and IL-18 after direct administration of DNA from apoptotic or healthy hepatocytes. Error bars indicate 1 SD.