Fig. 6.
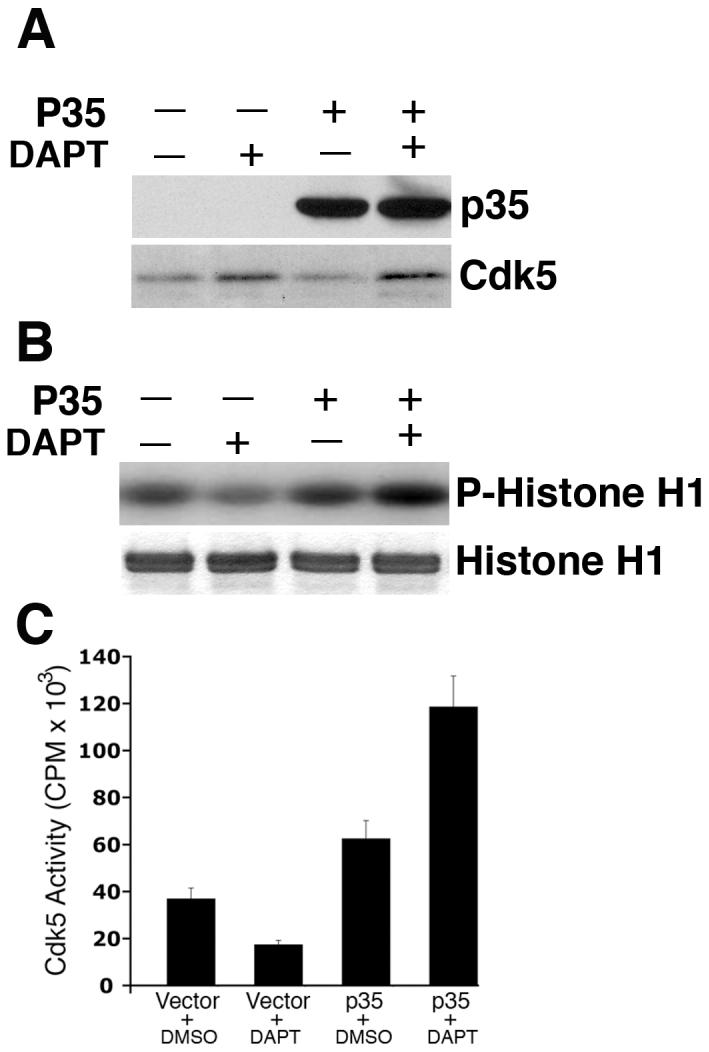
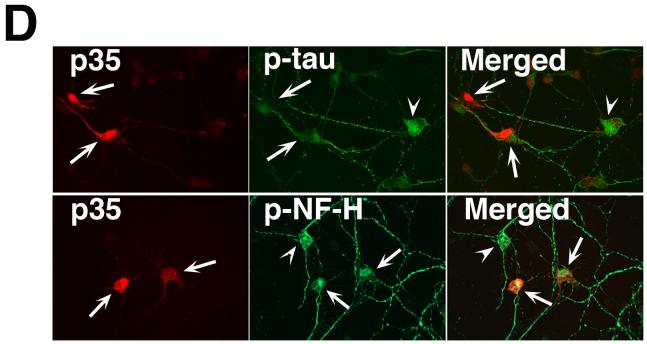
DAPT-induced attenuation of cdk5 activity and relocalization of p-tau and p-NF-H is reversed upon p35 overexpression. E18 rat embryonic cortical neurons were cultured for 7 d in B27/neurobasal medium. Neurons were transfected with either pCDNA3.1 vector or pCDNA3.1-p35 plasmid. Twenty four hours post-transfection, cells were treated with DAPT. Cells were processed 24 h after DAPT treatment for immunoblot analyses using anti-p35 antibody to detect p35 expression. (A) Immunoblot shows significant increase in p35 levels in the cells transfected with pCDNA3-p35 compared to that in the empty vector-transfected cells. Note that although in this exposure time of the film, endogenous p35 in the vector-transfected neurons is not detectable, a longer exposure shows the presence of endogenous p35 in the first two lanes, where signals of the overexpressed p35 in the last two lanes distort the blot to have a clean figure for presentation. The bottom panel shows the cdk5 expression level in the vector- transfected and p35-transfected cells treated with either DMSO or DAPT. (B) Overexpression of p35 by transfection rescues DAPT-induced downregulation of cdk5 activity. Upper panel shows the autoradiogram of phosphorylated Histone H1 substrate used in the kinase assays; bottom panel shows the source of the autoradiogram, the Coomassie blue-stained Histone H1 in the SDS-PAGE gel. (C) Scintillation counting of the phospho-Histone H1 protein cut out from the SDS-PAGE gels after autoradiography shows the relative extent of Histone H1 phosphorylation representing cdk5 activity in the empty vector-transfected and p35-transfected neurons treated with either DMSO or DAPT. Data are derived from three separate experiments. (D) Immunocytochemical analyses were also performed to detect p-tau and p-NF-H in DAPT-treated and p35-transfected E-18 rat cortical neurons. Immunostaining for p35 (red) and p-tau (green, upper panel) or p-NF-H (green, lower panel) demonstrates that p35 overexpression can reverse the DAPT-induced translocation of p-tau and p-NF-H to the soma (arrows). Neurons overexpressing p35 (arrows) show relatively less p-tau (arrows) staining in the soma compared to the untransfected neuron (arrowhead). Partial rescue (from the soma) occurred for p-NF-H upon p35 transfection (bottom panel). Neurons overexpressing p35 (arrows) show relatively less p-NF-H staining in the soma (arrows) compared to the untransfected neuron (arrowhead).