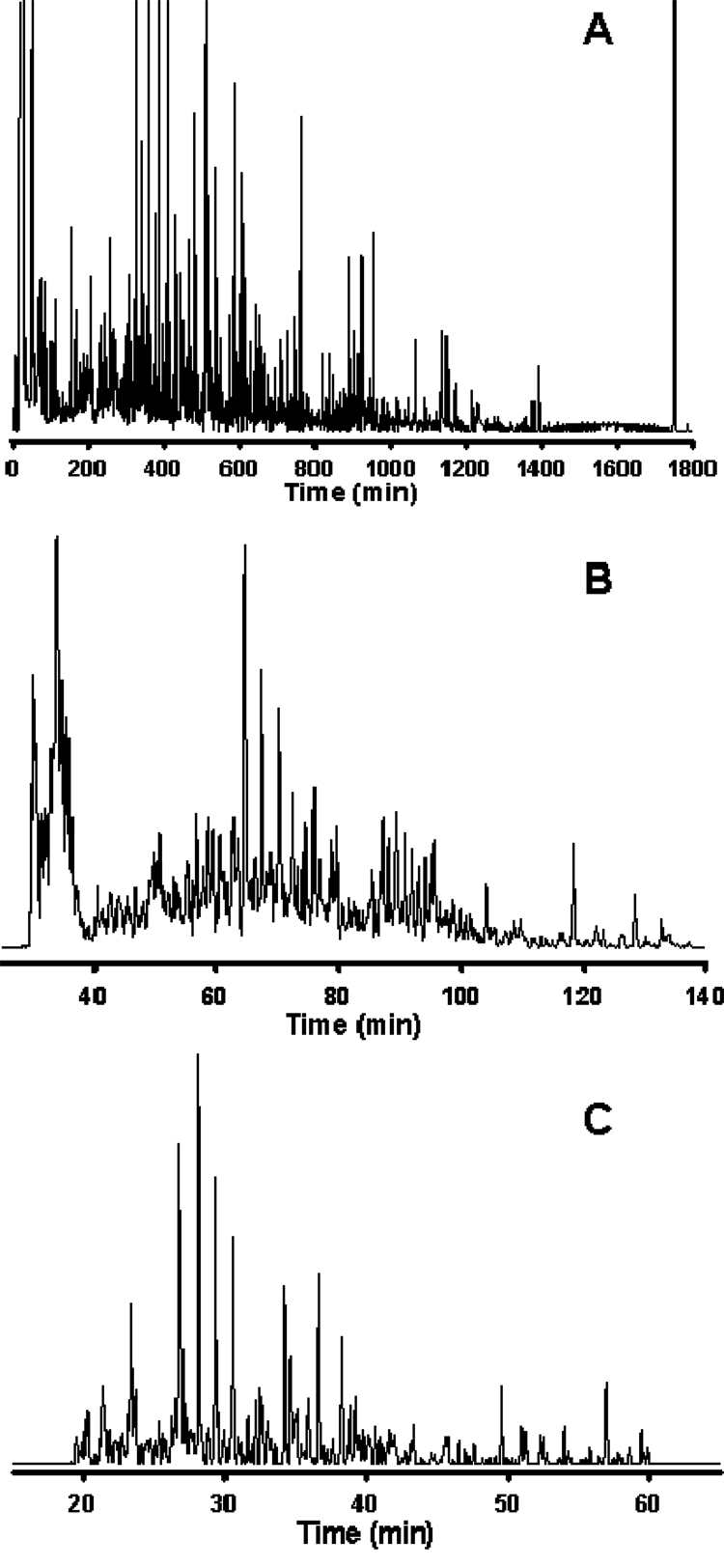
Figure 1. Analysis of the Shewanella oneidensis metabolome utilizing reversed-phase capillary LC coupled with FTICR MS.
Cells of S. oneidensis were lysed via bead-beating and the metabolome extracted using cold (−20°C) acetone with concomitant protein precipitation and removal via centrifugation. The supernatant containing the extracted metabolome was dried in vacuo and reconstituted in Nanopure water prior to sample injection. The LC conditions were as follows: operating pressure of 20,000 psi; mobile phase A consisted of 0.2% acetic acid + 0.05% trifluoroacetic acid in water; mobile phase B consisted of 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid in 90% acetonitrile + 10% water; gradient elution was by exponential gradient as a result of constant pressure operation. The MS detector consisted of an 11 Tesla FTICR MS utilizing home-built ion transmission optics, which was operated in the mass range of 100–1500 m/z. Reversed-phase C18 capillary columns: (A) 50 µm i.d. × 2 m, 3 µm dP, (B) 50 µm i.d. × 50 cm, 2 µm dP, (C) 50 µm i.d. × 20 cm, 1.4 µm dP. Peak-capacities of ~1500, ~500, and ~350 were calculated for the separations shown in A, B, and C, respectively. Figure 1A reproduced with permission from Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 3090–3100. Copyright 2005 American Chemical Society. Figures 1B and 1C unpublished data.