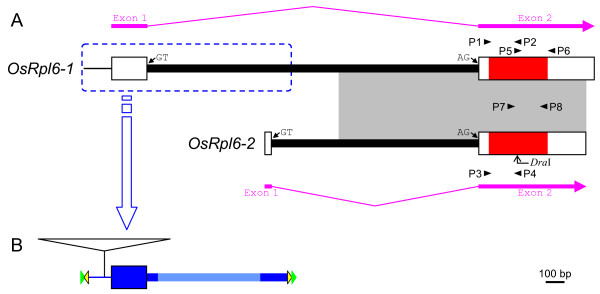
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the rice mitochondrial rpl6 genes, OsRpl6-1 and OsRpl6-2. (A) The exon-intron structures of OsRpl6-1 and OsRpl6-2. Exons and introns are represented by boxes and thick lines, respectively. In the exons, the RPL6-protein coding regions are colored with red, whereas the 5'- and 3'-untranslated regions (UTRs) are colored with white. The 5'-nontranscribed spacer upstream of the OsRpl6-1 exon 1 is indicated by a thin line. The GT and AG dinucleotides at the border of the intron are indicated by small arrows. The direction of each OsRpl6-1 and OsRpl6-2 transcript is indicated by a thick pink arrow joined with a thin pink broken line. A homologous region in the two rpl6 genes is shaded. The locations of primers P1-P8 are indicated by small arrowheads. The position of the DraI site in OsRpl6-2 is indicated by a bent arrow. The location of transposable elements (TEs) is enclosed with a blue dotted outline, and the structures are shown below. (B) Structure of TEs in OsRpl6-1. Blue and pale blue coloring, respectively, represent well-conserved and poorly-conserved regions among various rice sequences (Figs. 4 and 5). Potential terminal inverted repeat (TIR) and target site duplication (TSD) are indicated by yellow and green triangles, respectively (not to scale). An insertion of the Mutator-like element within the 5'-nontranscibed spacer region is indicated by an open triangle.