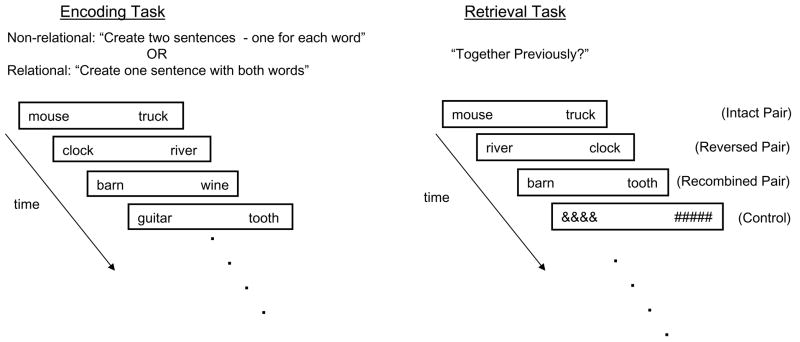
Figure 1.
Experimental design. Subjects encountered word pairs and were instructed to covertly create sentences. During non-relational encoding, subjects were instructed to covertly generate two sentences, one for each word. During the subsequent test phase, participants encountered word pairs and were instructed to decide whether the words had be shown ‘together previously?’ (i.e., relational retrieval). During relational encoding, subjects were instructed to covertly generate one sentence that included both words. Similarly, participants were then instructed to decide whether the words had be shown ‘together previously?’ (i.e., relational retrieval). All four non-relational runs were completed before the four relational runs. Test lists consisted of pairs of words previously seen together (Intact Pairs [IP]), pairs of words previously seen together, but in the reversed presentation order (Reversed Pairs [RevP]), and pairs of words previously seen, but not together (Recombined Pairs [RecP]). Both encoding and retrieval tasks were performed in the scanner, but only the retrieval task was scanned.