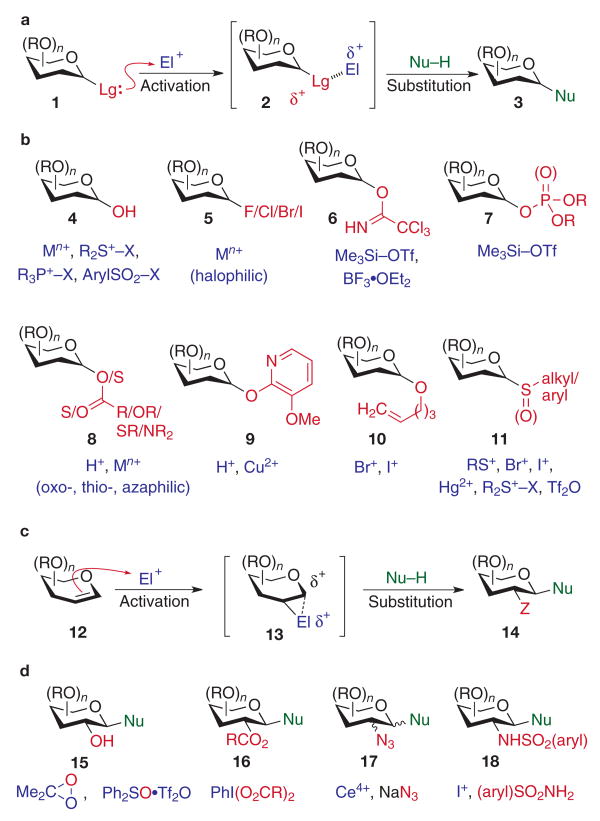
Figure 1. Glycosylation methods.
a, b, Glycosylation of acetal-derived glycosyl donors. Activation of the anomeric leaving group (Lg, red) with an electrophilic promoter (El+, purple) is followed by nucleophilic attack of the acceptor (Nu–H, green) on the resulting electron-deficient anomeric carbon of the carbohydrate donor. c, d, Glycosylation with glycal donors. Activation of glycals with various electrophiles (El+) is followed by coupling with a glycosyl acceptor (Nu–H) at the anomeric carbon. These glycosylations result in functionalization of both the C1 and C2 positions of the donor. M, metal; R, various substituents; Tf, trifluoromethanesulphonyl; X, various leaving groups; Z, various functionalities.