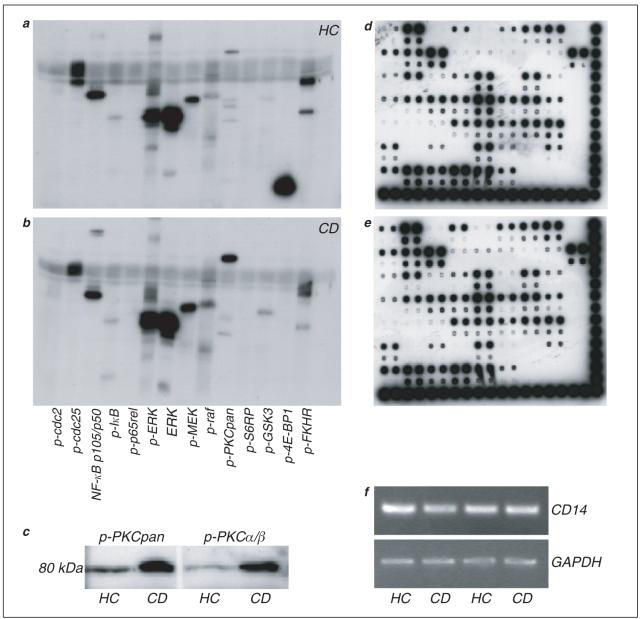
Fig. 3.
Signal transduction, transcriptional activity and gene expression in exuded leukocytes. a, b. Representative western blots illustrating phosphorylation status of a panel of cytoplasmic proteins in cells recovered 24 h after trauma in a healthy control (a; n = 5) and Crohn’s patient (b; n = 5). c. The most consistent abnormality in Crohn’s patients (CD) was hyperphosphorylation of PKC, and specifically PKC α/β, compared to healthy controls (HC). d, e. DNA-binding activity of various transcription factors from nuclear extracts. Representative membranes (n = 4) are shown from a healthy control (d) and a Crohn’s patient (e), in both of whom the same 44 factors could be detected. (f) Expression of mRNA in exuded cells from 4 subjects. Reverse transcriptase-PCR was performed for CD14 and GADPH, levels of which were similar in all samples. Of the 54 proteins assayed, the activity of 44 could be detected (Fig. 3 d, e). A total of 4 subjects (2 healthy; 2 Crohn’s patients) were compared with minimal variability detected between individuals.