Figure 4. Mechanisms of oxidation of LDL.
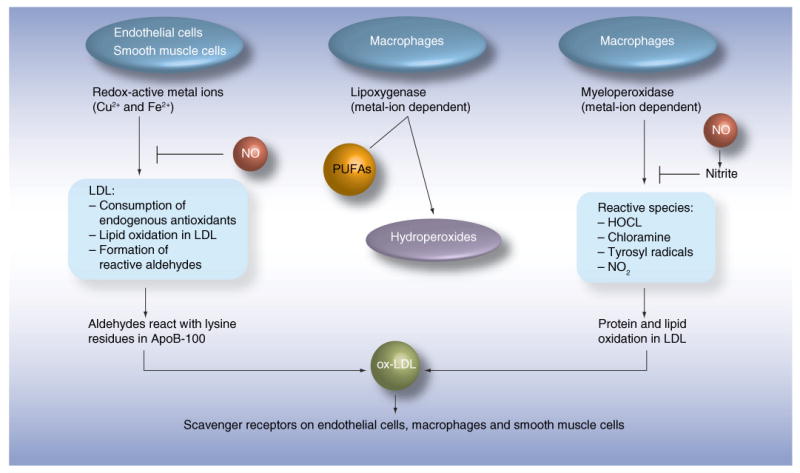
Several cell types and cell-mediated enzymatic reactions can lead to the oxidation of LDL. The common process is the formation of aldehydes, which interact with lysine residues in the ApoB100 protein in LDL. The antibody 4E6 is directed against a conformational epitope generated by this interaction. Interestingly, not only cells in the vessel wall, but also cells in adipose tissues, mediate oxidation reactions. Arrows indicate activation and flat ends indicate inhibition. HOCL: Hypochlorous acid; NO: Nitric oxide; ox-LDL: Oxidized LDL; PUFA: Polyunsaturated fatty acid.
