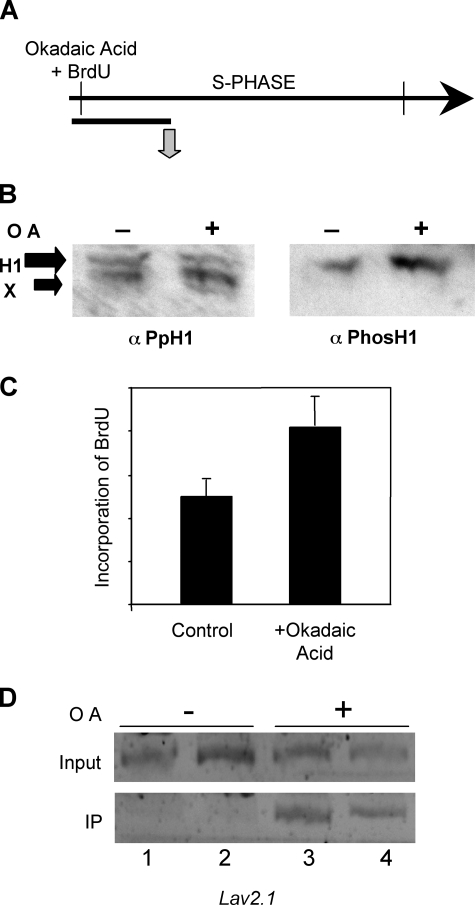
FIGURE 5.
Phosphorylation of H1 facilitates linker histone removal and firing of replication origins. A, experimental scheme. Macroplasmodia were treated with okadaic acid as described under “Experimental Procedures” and then analyzed 1 h after the beginning of S phase. B, okadaic acid induces hyperphosphorylation of H1. Western blot analyses of nuclei prepared from macroplasmodia either untreated (–) or treated (+) with okadaic acid. The blots were probed with an anti-PpH1 antiserum then stripped and reprobed with anti-phospho-H1 antibodies. C, okadaic acid treatment accelerates global DNA replication. The effect of okadaic acid treatment on replication was determined by incorporation of BrdUrd and dot blot analyses of genomic DNA with an anti-BrdUrd antibody, and blots were quantified with image quant. D, phosphorylation of H1 regulates replication timing. Replication of Lav2.1 was monitored by immunoprecipitation (IP) of BrdUrd containing DNA as described in Fig. 3. Note lanes 1 and 3 and lanes 2 and 4 correspond to DNA digested with EcoRI and HindIII, respectively prior to immunoprecipitation.