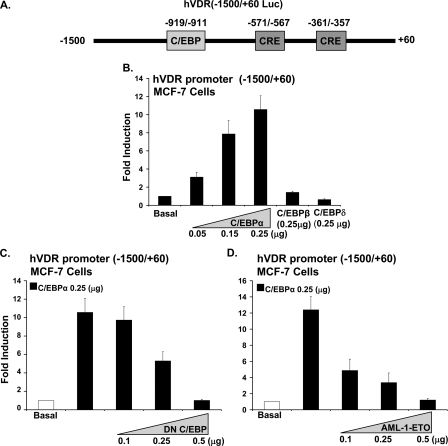
FIGURE 2.
Enhancement of hVDR promoter transcription by C/EBPα in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. A, schematic of the luciferase construct of the human VDR promoter -1500/+60, including a putative C/EBP motif and two putative CRE sites. B, MCF-7 cells were co-transfected with hVDR promoter and increasing concentrations of C/EBPα (0.05 μg to 0.25 μg) or 0.25 μg of C/EBPβ or C/EBPδ. C/EBPα (0.05, 0.15, and 0.25 μg) results in a significant induction in hVDR promoter activity (p < 0.05 compared with basal). C and D, suppression of hVDR promoter transcription using DN C/EBP or AML-1/ETO. MCF-7 cells were co-transfected hVDR promoter, 0.25 μg of C/EBPα and increasing concentrations of DN C/EBP or of AML-1/ETO, a C/EBPα inhibitor. Empty vectors were used to keep the total DNA concentrations the same. In MCF-7 cells there was no effect of DN CEBP or AML-1/ETO at the concentrations used on basal levels of hVDR transcription. pRL-TF-Renilla luciferase was co-transfected as an internal control. Results of three or more separate experiments are presented (mean ± S.E.). Co-transfection with 0.25 μg or 0.5 μg of DN C/EBP or 0.1, 0.25, or 0.5 μg of AML-1/ETO resulted in a significant decrease in C/EBPα-induced VDR transcription (p < 0.05 compared with cells transfected with C/EBPα (0.25 μg) alone).