FIG. 1.
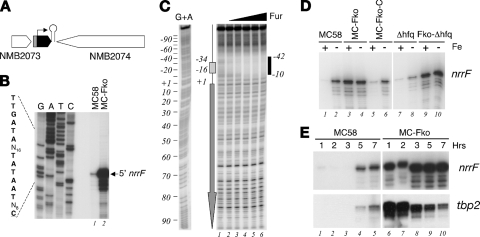
(A) Diagrammatic representation of the locus containing the nrrF gene in MC58. The Fur-regulated promoter is indicated in gray, the orientation of the sRNA is indicated with a black arrow, and the relative position of the rho-independent transcriptional terminator is marked with a hairpin loop. (B) Mapping of the 5′ end of the nrrF transcript by primer extension. Portions (20 μg) of total RNA prepared from cultures of the wild type (MC58) and Fur-null mutant (MC-Fko) grown to mid-logarithmic phase under iron-replete conditions were hybridized with the sR-p7 primer (Table 1) and elongated with reverse transcriptase. The elongated primer band mapping the 5′ end of the sRNA transcript is indicated. Sequence reactions (G, A, T, and C) were performed with the same primer on plasmid pGemsRNA1/2 as a template. The corresponding +1 nucleotide of transcriptional initiation and the upstream promoter sequences are indicated on the left. (C) DNase I footprinting analysis with purified meningococcal Fur protein and a radioactively labeled 245-bp DNA probe, 5′ end labeled at the EcoRI site, corresponding to the nrrF promoter region. The probe was incubated with increasing concentrations of Fur protein: lanes 1 to 6 correspond to concentrations of 0, 14 nM, 44 nM, 130 nM, 392 nM, and 1.2 μM concentrations of Fur protein. A G+A sequencing reaction (19) of the probe was performed and run in parallel as a molecular weight ladder. The box and arrow to the left show the position and the direction of the Fur-box and nrrF gene, respectively. The Fur-protected region is indicated to the right as a vertical black bar, and the numbers indicate the boundaries of the binding site with respect to the +1 transcriptional initiation site. (D) Regulation of NrrF transcription. Total RNA was prepared from the wild type (MC58), the Fur-null mutant (MC-Fko), its complemented derivative (MC-Fko-C), the Hfq mutant (Δhfq), and the Fur and Hfq double mutant (Fko-Δhfq) grown to mid-log phase under iron-replete conditions before (+) and after (−) 15 min of treatment with iron chelator (2,2′-dipyridyl). Then, 10 μg of RNA from each strain was reverse transcribed with the sR-p7 primer, and the relative quantities of extended primer product are shown from a single representative experiment. (E) Time course experiment in which cultures of MC58 and MC-Fko strains were grown in iron-replete conditions and total RNA was extracted after 1, 2, and 3 h (logarithmic phase) and 5 and 7 h (stationary phase). The relative quantities of NrrF and tbp2 transcripts were analyzed from 10 μg of each total RNA sample by quantitative primer extension and S1 nuclease assay, respectively.