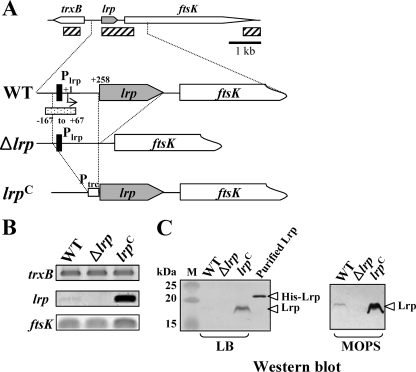
FIG. 1.
Analysis of Lrp expression in the wild-type (WT, χ3761), Δlrp (χ9411), and lrp(Con) (χ9448) strains. (A) Schematic diagram of the lrp regions in the Salmonella strains described in the text (hatched box, amplified DNA regions used by RT-PCR; closed boxes, Lrp-binding motif, −79 to −64; dotted box, DNA fragment for EMSA). The coordinates in the picture are numbered with respect to the lrp transcription start site (+1) (66). (B) RT-PCR analysis of the trxB, lrp, and ftsK transcripts from mid-exponential-phase cells grown in LB broth. The images were inverted to intensify the DNA bands. Data are one of two similar RT-PCR results using two independent RNA isolations as a template. (C) Expression of Lrp in the Salmonella strains. Bacterial cells were grown in LB or MOPS minimal medium overnight at 37°C. Whole-cell proteins were resolved on SDS-PAGE (12%) gels. Proteins in the gels were transferred to nitrocellulose for Western blot analysis. Lrp was detected using mouse anti-Lrp serum. Purified His-tagged Lrp protein was used as positive control for the Western blot. Lane M, dual-color prestained protein standards (Bio-Rad).