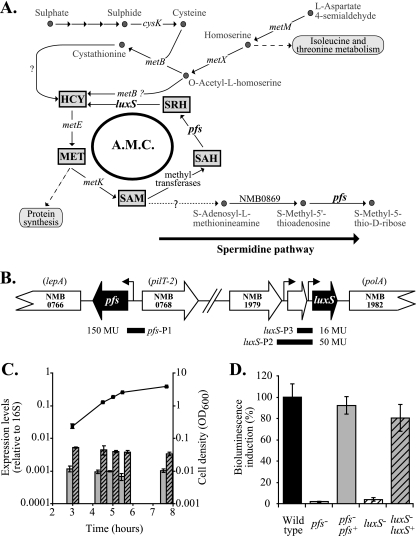
FIG. 1.
Pfs function and expression in N. meningitidis. (A) Pathways involved in the synthesis of sulfur-containing amino acids (based on the findings of Sekowska et al. [24] and analysis of the previously published N. meningitis genomes). Both Pfs and LuxS contribute to the AMC, a recycling pathway linked to the last steps of de novo methionine and SAM synthesis. Pfs is also involved in the polyamine pathway (with concomitant production of methyl-5′-thioadenosine, which is then transformed into adenosine). cysK, NMB0763; luxS, NMB1981; metB, NMB0802; metE, NMB0944 (misannotated metH); metK, NMB1799; metM, NMB1228; metX, NMB0940; pfs, NMB0767. Arrows indicate reactions that have not been established in N. meningitidis yet or for which no genes have been identified. MET, methionine. (B) The genome sequences of N. meningitidis strains (TIGR) show that pfs is located upstream of lepA on the same DNA strand and upstream of pilT-2 on the opposite DNA strand. A 260-bp fragment encompassing the predicted promoter region upstream of the pfs start codon (pfs-P1) was used to express lacZ and pfs in reporter assays and complementation studies, respectively. The luxS gene is potentially organized in an operon with the two upstream open reading frames (encoding hypothetical proteins); downstream of luxS is the gene encoding DNA polymerase I. A 560-bp fragment (lux-P3) and a 270-bp fragment (lux-P2) containing predicted promoter regions for luxS were used to express a lacZ reporter, and the shorter promoter was also used to express luxS in a complementation study. Levels of expression of the lacZ translational fusions constructed with the different promoters (P) are expressed in Miller units (MU). (C) Relative pfs and luxS transcript levels determined by RT-PCR using cDNA prepared from mRNA samples obtained at different time points during growth of N. meningitidis wild-type strain B16B6 in BHI and using 16S rRNA as an endogenous, constitutive control. (D) AI-2 bioassays. Double-filtered supernatants of BHI cultures of N. meningitidis wild-type strain B16B6 (black bar), mutant B16B6-pfs (open bar), complemented mutant B16B6-pfs pfs+ (gray bar), mutant B16B6-luxS (open striped bar), and complemented mutant B16B6-luxS luxS+ (gray striped bar) were tested to determine their abilities to induce the bioluminescence of the bioreporter V. harveyi BB170 using sterile BHI broth as a blank, as described in Materials and Methods Wild-type levels of bioluminescence were defined as 100% (control level). Induction of bioluminescence was proportional to the presence of AI-2 in supernatants. All experiments were repeated at least three times. The error bars indicate standard errors.