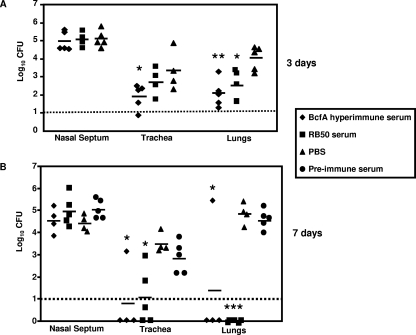
FIG. 4.
Effect of adoptive transfer of BcfA-specific sera on respiratory tract colonization. Mice were intraperitoneally injected with anti-BcfA hyperimmune serum, convalescent-phase anti-RB50 serum, preimmune serum, or sterile PBS. Three to 4 h later, mice were intranasally challenged with 5 × 105 CFU of RB50 in a 25-μl volume. Three (A) and 7 (B) days postchallenge, mice were sacrificed and bacterial colonizations in the nasal septums, tracheas, and lungs were determined. Dashed line represents lower limits of CFU detection. Individual symbols represent a single mouse. Black bars represent mean colonization of respective group. The unpaired two-tailed Student t test was used to determine statistical significance. The groups of mice receiving anti-BcfA hyperimmune serum and convalescent-phase anti-RB50 serum were compared to those groups receiving sterile PBS. The asterisks indicate the range of the different P values (one asterisk, ≤0.05; two asterisks, ≤0.005; three asterisks, ≤0.0005). Differences between the CFU obtained from preimmune-treated mice and PBS-treated mice were not statistically significant.