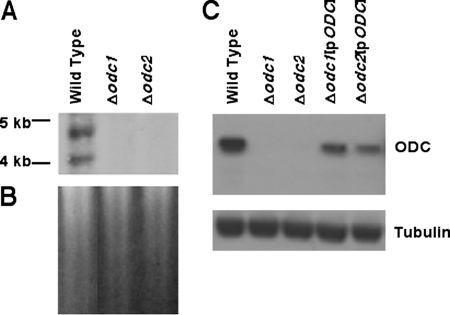
FIG. 2.
Molecular characterization of the ODC locus and ODC expression in the Δodc knockouts. Genomic DNA from wild-type, Δodc1, and Δodc2 parasites and protein lysates from wild-type, Δodc1, Δodc2, Δodc1[pXG-BSD-ODC], and Δodc2[pXG-BSD-ODC] parasites were obtained by standard protocols. (A) 2 μg of genomic DNA from wild-type, Δodc1, or Δodc2 parasites was digested with SalI and hybridized to a 1.0-kb fragment of the ODC coding region that was prepared by PCR. Molecular size markers are indicated to the left. (B) Ethidium bromide-stained gel that was employed in the Southern blot in panel A. (C) Cell extracts prepared from 1.0 × 107 wild-type, Δodc1, Δodc2, Δodc1[pXG-BSD-ODC] (Δodc1[pODC]), or Δodc[pXG-BSD-ODC] (Δodc2[pODC]) promastigotes were fractionated by sodium dodecyl sulfate electrophoresis and the blots probed with polyclonal antibodies against L. donovani ODC and a commercial monoclonal antibody that recognizes tubulin. The tubulin antibody was employed to verify equivalent loading of protein on all lanes.