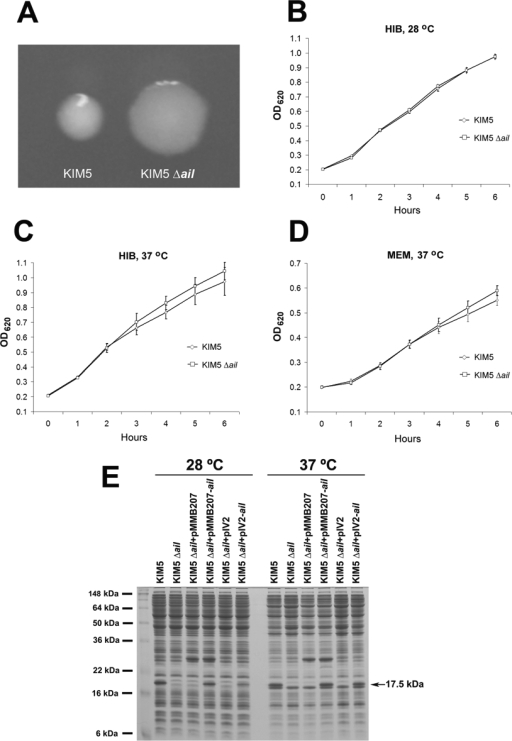
FIG. 1.
Colony morphology assessment, growth curve analysis, and complementation of a KIM5 Δail mutant. (A) Colony morphology of the strain KIM5 and a KIM5 Δail mutant grown on HIB agar. KIM5 forms smaller, shinier colonies, while the Δail mutant is flatter, wider, and more opaque and has rougher colony edges. (B to D) Growth curve analysis of KIM5 and the Δail mutant under various growth conditions. (E) Deletion and complementation of ail was confirmed by SDS gel electrophoresis. Y. pestis KIM5 and derivative strains were grown overnight in HIB at 28°C or 37°C. For pMMB207-containing strains, 100 μM IPTG was added to induce ail expression. pIV2 is a plasmid derived from Yersinia enterocolitica that can be stably maintained during in vivo experiments for ail complementation (59). The identity of the 17.5-kDa band absent in the KIM5 Δail mutant was confirmed to be Ail protein by mass spectrometry at the University of Michigan Proteomics Consortium.