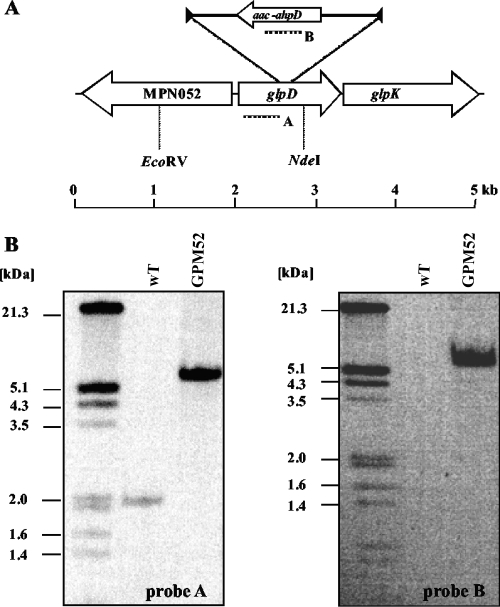
FIG. 4.
Isolation of a M. pneumoniae glpD transposon insertion mutant. (A) Schematic representation of the genomic region of the glpD gene in M. pneumoniae and the site of the transposon insertion in the glpD mutant strain GPM52. Probes hybridizing to internal fragments of the glpD and the aac-ahpD genes are depicted as dotted lines. (B) Southern blot analysis to confirm the unique insertion of the minitransposon into the glpD gene of strain GPM52. Chromosomal DNAs of the wild-type (WT) and mutant (GPM52) strains were digested using EcoRV and NdeI. Blots were hybridized with the glpD-specific probe (left) and a probe hybridizing to the aac-ahpD gene of the minitransposon (right). DIG-labeled DNA molecular mass marker III (Roche Applied Science) served as a standard.