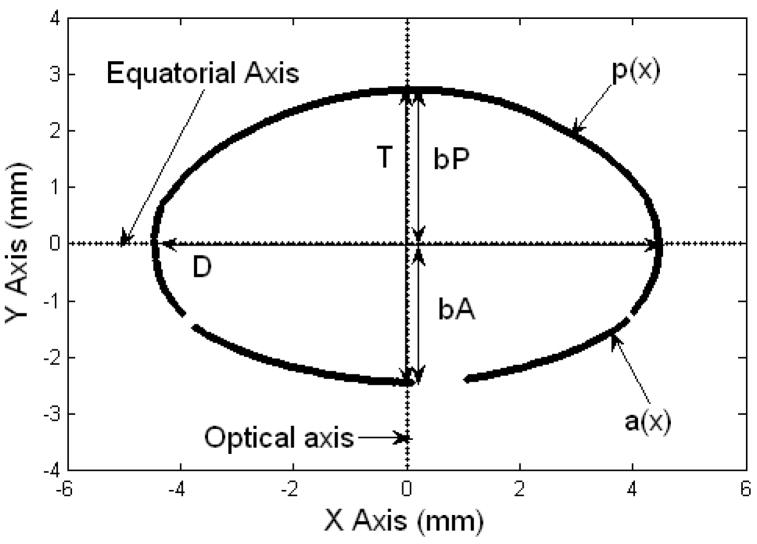
Figure 2.
The coordinate system of the Two Curves method. The equatorial axis is parallel to the X axis and the optical axis is parallel to the Y axis. The anterior surface of the lens is positioned in the 3rd and 4th quadrants of the co-ordinate system and the posterior surface in the 1st and 2nd quadrants. The data set of pixel coordinates above the equatorial axis corresponds to the posterior segment of the lens, and the set below, corresponds to the anterior segment of the lens. The diameter (D), thickness (T), anterior thickness (bA) and posterior thickness (bP) are shown. p(x) is the posterior TCM polynomial and a(x) is the anterior TCM polynomial. Gaps on the lens surface are regions where the edge detection algorithm could not identify the lens profile.