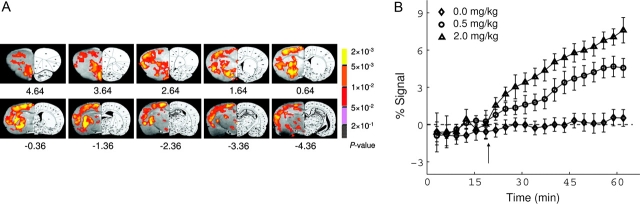
Fig. 4.
(A) MEMRI of acute cocaine-induced brain activation. Activation maps are superimposed onto T2-weighted MRI with corresponding rat brain atlas sections shown on the right. Activated voxels are clustered in the hemisphere with the BBB disrupted by hyperosmolar mannitol. The contralateral hemisphere had an intact BBB and did not show activation. Activated structures include olfactory cortex; medial, ventral, and lateral orbital cortex; pre-limbic cortex; cingulate cortex; nucleus accumbens (NAc), caudate putamen; ventral pallidus; external globus pallidus; agranular insular cortex; thalamus; hypothalamus; retrosplenial dysgranular cortex; hippocampus; and primary and secondary somatosensory and motor cortex. (B) Averaged MEMRI response time course in the NAc from animals receiving saline (n = 6) and 0.5 mg/kg (n = 5) and 2.0 mg/kg (n = 6) cocaine. All time courses were normalized to the baseline signal after bolus injection of mannitol, but before the injection of cocaine or saline. Adapted with permission of Lu et al.46