Fig. 1.
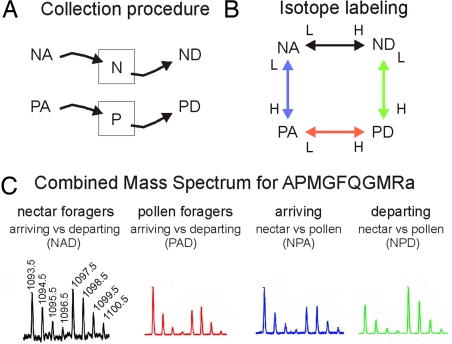
Experimental design and mass spectrometric results for analyzing changes in peptide profiles during honey bee foraging behavior. Honey bee colonies were kept in outdoor flight cages with separate ad libitum feeders for nectar (N, nectar; i.e., sugar solution) and pollen (P, pollen). (A) Foraging bees were collected at either feeder shortly after they landed and before they started to collect food (NA, PA; A, arriving) or after they had finished food collection and were ready to take off (ND, PD; D, departing). (B) Brain peptide samples from the various behavioral groups were labeled with different isotopes and compared. N and P “squares” refer to the feeders. (C) Mass spectrometric analysis of the isotopically labeled peptides, with the ratio of peak heights used to determine peptide level changes. Bee brain peptides were separated by using HPLC and directly analyzed by using an electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometer. The mass spectrum of APMGFQGMRa for each of the comparisons was obtained by summing the scans in the extracted ion chromatograms: NAD, arriving versus departing nectar foragers; PAD, arriving versus departing pollen foragers; NPA, arriving nectar versus arriving pollen foragers; NPD, departing nectar versus departing pollen foragers.