Fig. 10.
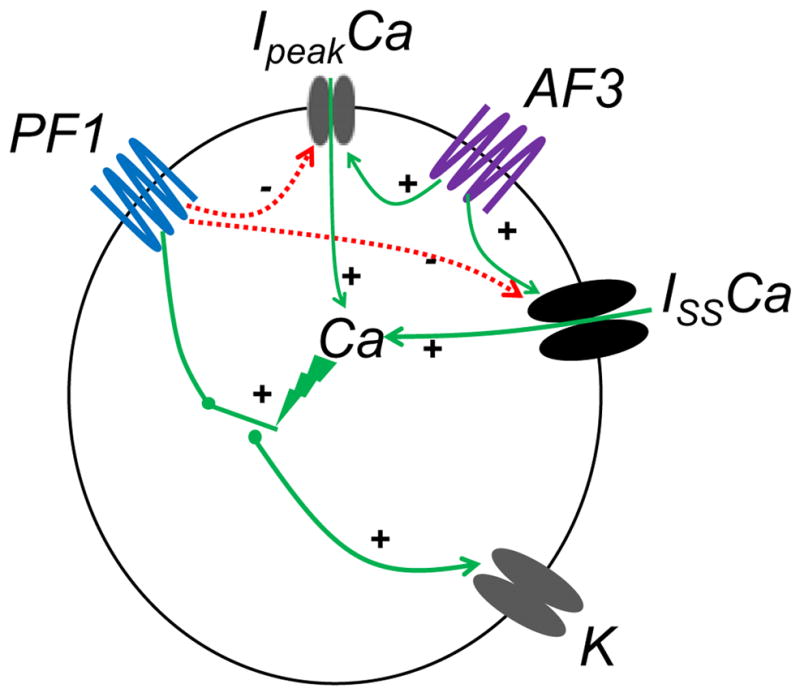
Summary diagram of the effects of PF1 and AF3 on voltage-activated currents. PF1 inhibits the opening of voltage-activated calcium channels (Ipeak and Iss) and stimulates opening of potassium channels (K) but only in the presence of calcium. AF3 stimulates opening of voltage-activated calcium channels (Ipeak and Iss). Calcium is required to allow the inhibitory effect of PF1 on potassium currents. If sufficient calcium is not present (for example due to the presence of cobalt in the bathing solution or if a high concentration of PF1 is used inhibiting the voltage-activated currents) the effect of PF1 on voltage-activated potassium current is prevented.
