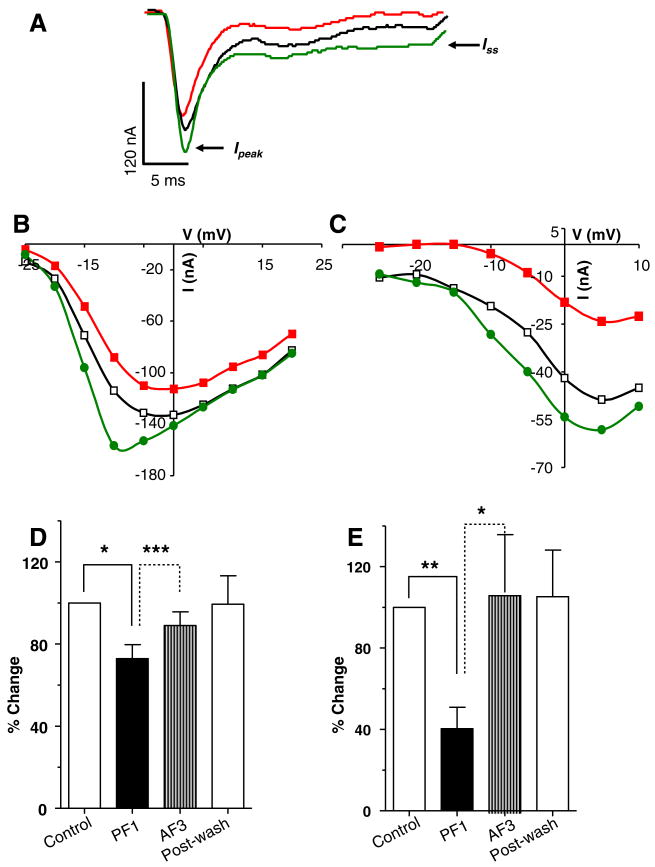
Fig. 8.
AF3 triggers the recovery of PF1-inhibited currents. (A) Voltage-activated inward currents records: control; PF1 (1 μM) (red) and; AF3 (1 μM). Note the decrease in amplitude of the Ipeak and the Iss currents after PF1 application and recovery of currents after AF3 application. Recordings were made in calcium-Ringer solution with cesium acetate in recording micropipettes. (B) Ipeak current step–voltage relationship for the experiment shown in (A). Control:
 PF1 (1 μM):
PF1 (1 μM):
 AF3 (1 μM):
AF3 (1 μM):
 Postwash:
Postwash:
 (C) Iss current step–voltage relationship for the experiment shown in (A). Control:
(C) Iss current step–voltage relationship for the experiment shown in (A). Control:
 PF1 (1 μM):
PF1 (1 μM):
 AF3 (1 μM):
AF3 (1 μM):
 Post-wash:
Post-wash:
 (D) Inhibition of the Ipeak current after PF1 and recovery after AF3 application (paired t-test, n = 5, **P ≤ 0.01, *P ≤ 0.05). (E) Inhibition of the Iss current after PF1 application and recovery after AF3 application. Note that AF3 potentiated the Iss current (paired t-test, n = 5, **P ≤ 0.01, *P ≤ 0.05).
(D) Inhibition of the Ipeak current after PF1 and recovery after AF3 application (paired t-test, n = 5, **P ≤ 0.01, *P ≤ 0.05). (E) Inhibition of the Iss current after PF1 application and recovery after AF3 application. Note that AF3 potentiated the Iss current (paired t-test, n = 5, **P ≤ 0.01, *P ≤ 0.05).