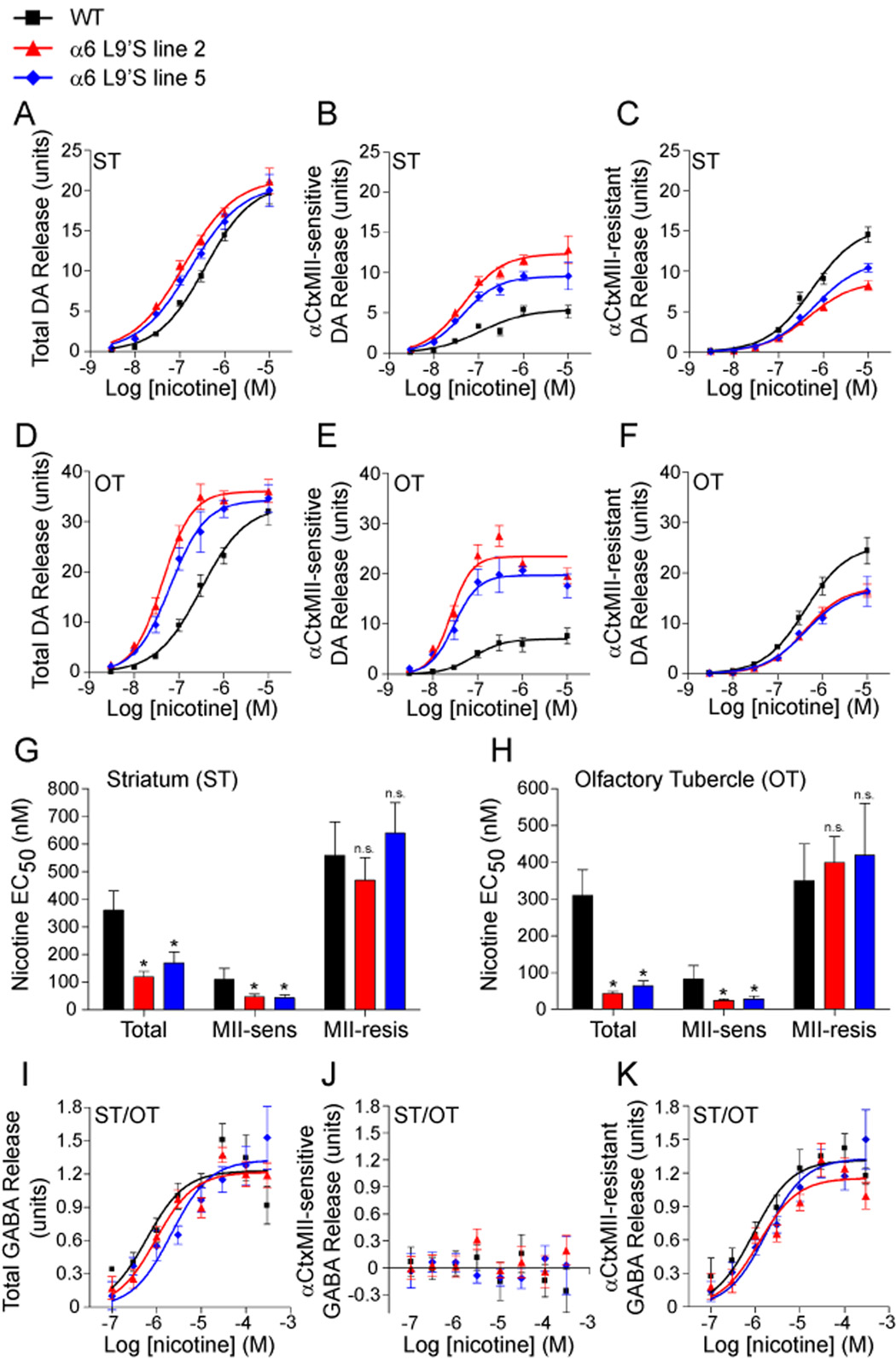
Figure 2. Presynaptic α6* nAChRs in striatum mediate hypersensitive, nicotine-stimulated DA release in α6L9’S transgenic mice.
(A–C) Hypersensitive DA release in striatum of α6L9’S transgenic mice is α6*-dependent. Striata (‘ST’; dorsal striatum and dorsal aspects of nucleus accumbens) from WT and α6L9’S mice were dissected and synaptosomes were prepared. DA release was stimulated with a range of nicotine concentrations (3 nM, 10 nM, 30 nM, 100nM, 300 nM, 1 µM, 10 µM), and a concentration-response relation for each mouse line (n = 6 mice / line) is shown for total release (A). To determine the relative contribution of α6* and non-α6* receptors, striatal synaptosome samples were incubated with αCtxMII (50 nM). α6* independent release is shown in (C), and αCtxMII-sensitive (α6* dependent) release is shown in (B).
(D–F) Hypersensitive DA release in olfactory tubercle of α6L9’S transgenic mice is α6*-dependent. Olfactory tubercle (‘OT’) was dissected from WT and α6L9’S mice, and samples were processed as in (A–C).
(G and H) Quantification of hypersensitive DA release in striatum (G) and olfactory tubercle (H). Average nicotine EC50 values for each concentration response curve from (A–F) are shown.
(I–K) α6* nAChRs do not participate in nicotine-stimulated GABA release in striatum. ST and OT were dissected and combined, followed by synaptosome preparation. GABA release was stimulated by nicotine at the following concentrations: 100 nM, 300 nM, 1 µM, 3 µM, 10 µM, 30 µM, 100 µM, and 300 µM. Total (I) release, and αCtxMII-sensitive (J) and resistant (K) components are shown.
Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. *, p < 0.05.