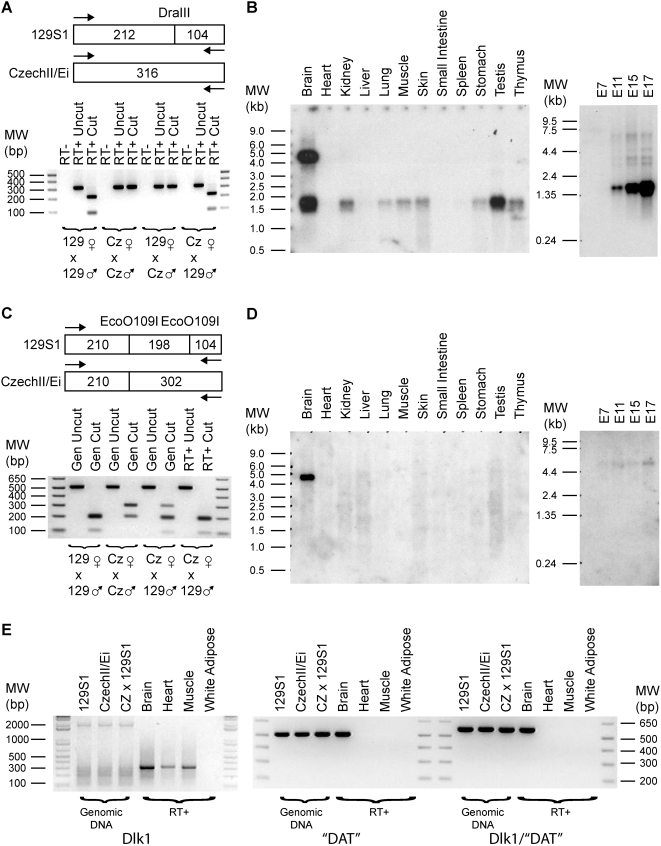
Figure 3. Dlk1 is paternally expressed and has an abundant alternatively polyadenylated transcript in the mouse brain.
(A) A DraIII restriction site polymorphism between 129S1 and CzechII/Ei mice was utilized to determine that Dlk1 is paternally expressed. PCR primers were Dlk1 2Up/317Dn. (B) Northern analysis using the same Dlk1 PCR fragment as probe revealed that Dlk1 is widely expressed. Of the tissues investigated, only the adult brain is characterized by having an additional and abundant transcript that is roughly 4.5 kb in length. (C) Several ESTs cluster to the syntenic region of “DAT” (Dlk1 associated transcript). RT-PCR was done with “DAT” primers 1533Up/2044Dn. Using a EcoO109I restriction site polymorphism, “DAT” was shown to be like Dlk1 in its paternal expression. (D) Northern analysis on adult tissue samples of “DAT” detected a 4.5 kb transcript only in the brain. This band is identical in size to the long transcript of Dlk1 found in the brain. Moreover, the length of this transcript is greater than the distance (∼2.7 kb) between mouse Dlk1 polyA and “DAT” polyA. (E) RT-PCR was performed with various primer sets. Left most panel showed that Dlk1 is expressed in brain, heart and muscle. Middle panel shows that “DAT” is only detectable in brain and is consistent with Northern findings. For the right panel, PCR was performed with a primer set in which the upstream primer (Dlk1 1237Up) was before the canonical Dlk1 polyA site while the downstream primer was after this site (Dlk1 1805Dn). A band was detected only in the brain, indicating that “DAT” is an alternatively polyadenylated transcript of Dlk1. This result was confirmed by cDNA cloning (Accession numbers: EU434914-EU434917).