Figure 1.
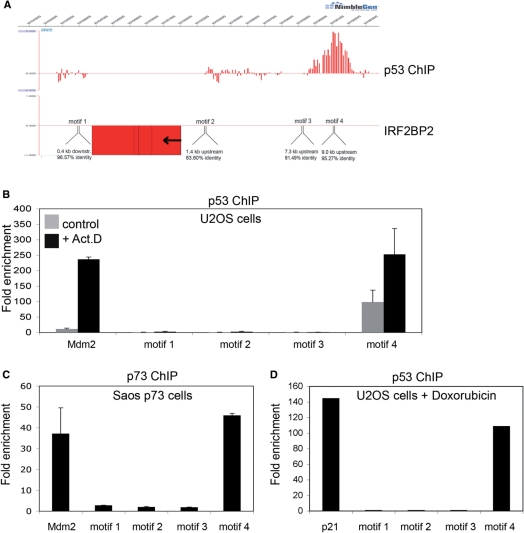
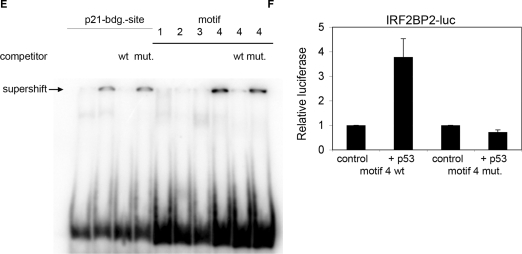
Identification of a p53-binding site upstream of the IRF2BP2 gene. (A) ChIP-on-chip profile from U2OS cells expressing p53. A region on chromosome 1 including the IRF2BP2 gene is visualized using Signalmap (Nimblegen Systems Inc.). Cells were treated with 5 nM Act.D for 24 h prior to chromatin isolation and ChIP with anti-p53 antibody. In the upper track the log 2 ratio of p53 ChIP material over input signal is shown. Every bar represents one probe on the array. The lower track displays the location of the IRF2BP2 gene including a schematic representation of p53 motifs identified by the p53MH algorithm in the vicinity of the IRF2BP2 gene. Also shown are their locations relative to the IRF2BP2 gene. Motif 4 corresponds to the p53-binding site previously identified by ChIP-on-chip. (B) Binding of endogenous p53 in U2OS cells to the putative p53-binding motifs. Cells were treated with 5 nM Act.D for 24 h or left untreated prior to chromatin isolation. Targeted ChIP was performed with primers for Mdm2 and for sequences spanning the predicted motifs. Shown is the enrichment in fold over the negative control (myoglobin). Error bars represent the standard deviation of three independent experiments. (C) Saos cells expressing p73α were induced with Doxycyclin for 24 h prior to treatment with 5 nM Act.D for another 24 h before chromatin was isolated. Targeted ChIP was performed using an anti-p73 antibody. Extent of binding of p73α was determined by RT-PCR with primers used in (B). Error bars represent the SD of three independent experiments. (D) U2OS cells were treated with 1 nM doxorubicin for 24 h, before chromatin was isolated. Targeted ChIP was done as in (B). (E) EMSA shows specific binding of p53 to the DNA-sequence containing motif 4. Labeled oligonucleotides spanning either the p53-binding site in the p21-promoter or DNA sequences of the IRF2BP2 surrounding regions containing the motifs 1–4 were incubated with in vitro translated p53. In all lanes except lane 1 p53-antibody was added to induce a supershift of the protein–DNA complexes. An unlabeled oligo containing the wild-type or a mutant p53-binding site of the p21-promoter was used as a competitor to show specificity of binding. (F) The motif 4 containing p53-binding site can function as an enhancer. Saos cells were transfected with a luciferase-construct containing either the wild-type or a mutant DNA sequence derived from motif 4, alone or together with p53. Shown is the fold activation of the IRF2BP2 luciferase construct over the vector alone. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three independent experiments.