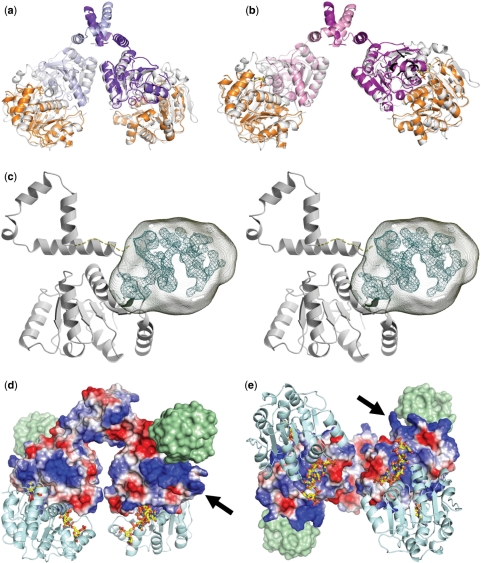
Figure 4.
Model for the dimeric Hera helicase and location of the RBD. (a, b) Construction of the Hera_1–419 dimers by superposition of the isolated Hera_N (PDB-ID 1gxs) and Hera_208–419 structures onto the Vasa-RNA complex. The view and color code for Hera_208–419 are the same as in Figure 2. Hera_N is colored orange, and the template Vasa is colored in white. (c) Stereo view of the location of the Hera RBD (residues 420–510) in crystals of Hera_208–510. Electron density from the MAD-phased tetragonal crystals is contoured at the 1σ level. This density is not explained by residues 208–419 and must thus belong to residues 420–510. The approximate volume for these residues is drawn as a transparent hull. The Hera_208–419 monomer is taken from dimer II and shown in gray. The connection between the Hera_208–419 C-terminus and the RBD is shown as a dashed line. (d) Electrostatic potential calculated for dimer II showing a distinct positively polarized patch (arrow) close to the RBD (location shown as a green surface). (e) View rotated 90° about the x-axis to emphasize the close proximity of the RNA-binding sites. The nucleotide AMP was taken from the Hera_N structure, the RNA from Vasa. Both are shown as stick models.