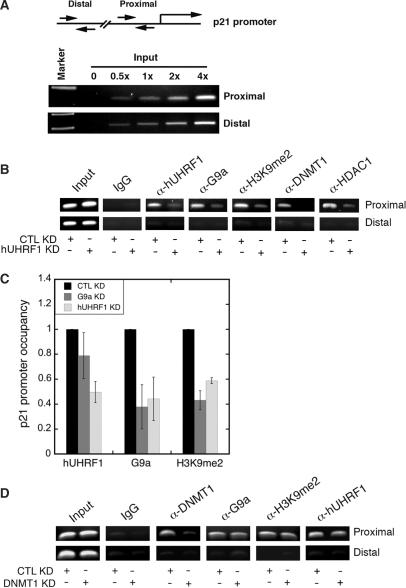
Figure 7.
hUHRF1 recruits G9a and other chromatin modification enzymes to p21 promoter. (A) Linearity of PCR amplification using primer sets for proximal (−385 to −240) and distal (−4164 to −3959) regions of p21 promoter with increasing amount of input DNA. (B) ChIP analysis of p21 promoter after KD of hUHRF1. HeLa cells were transfected with either control siRNA (CTL KD) or hUHRF1 siRNA (hUHRF1 KD). Using the chromatin isolated from the KD cells, ChIP was performed to detect the proteins or histone modification as indicated at the top of the panel. 5% input is shown. (C) Quantitative ChIP analysis for relative p21 promoter occupancy of hUHRF1, G9a and dimethylated H3K9 (H3K9me2) after KD of hUHRF1 or G9a. Q-PCR data of each group were normalized to its input as % input. The relative p21 promoter occupancy of hUHRF1 or G9a KD samples represents the fold change in percentage input over that of the CTL KD. Error bars indicate standard deviation of three independent experiments. (D) ChIP analysis of p21 promoter after KD of DNMT1. HeLa cells were transfected with either control siRNA (CTL KD) or DNMT1 siRNA (DNMT1 KD). CHIP was performed as described in (B) and 5% input is shown.