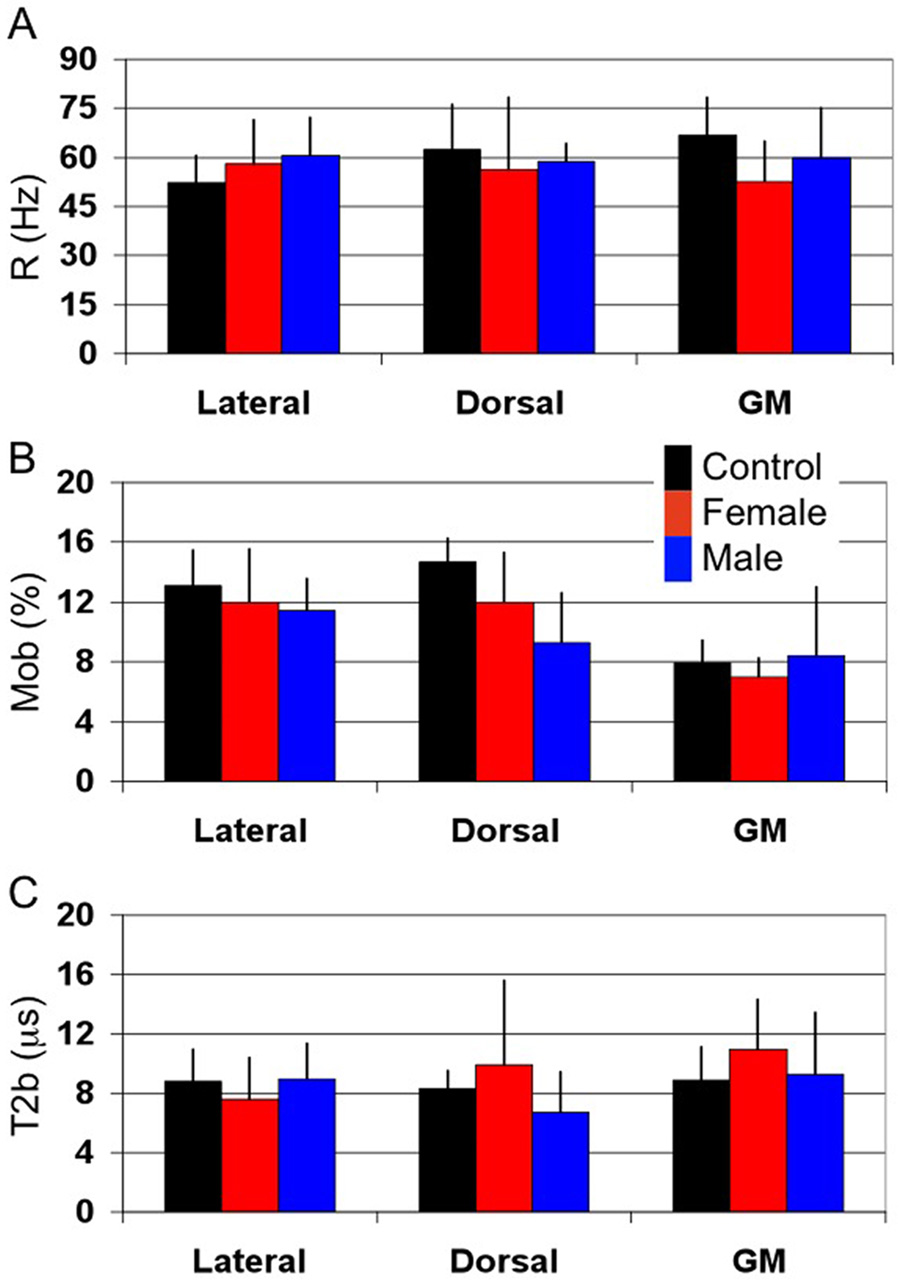
Figure 3.
Mean qMT metrics for controls (black), X-ALD females (red) and AMN males (blue) for each of the dorsal and lateral columns and dorso-lateral horn gray matter. (A) Rate of MT exchange (R) in Hz. R is approximately the same for all volunteers and subjects with AMN for each of the columns and GM. (B) Fraction of bound spins (Mob). Mob is seen to decrease in the dorsal column, which is the principle site of pathology, in AMN patients as compared to healthy controls. Similarly, a significant difference between WM and GM Mob can be appreciated. (C) Transverse relaxation time of bound spins (T2b). T2b is approximately the same for all subjects studied. However, the large variability in T2b for the X-ALD females in the dorsal column could be a result of hydrophobic interactions with bulk water caused by increase in very long chain fatty acid incorporation into the myelin membrane.