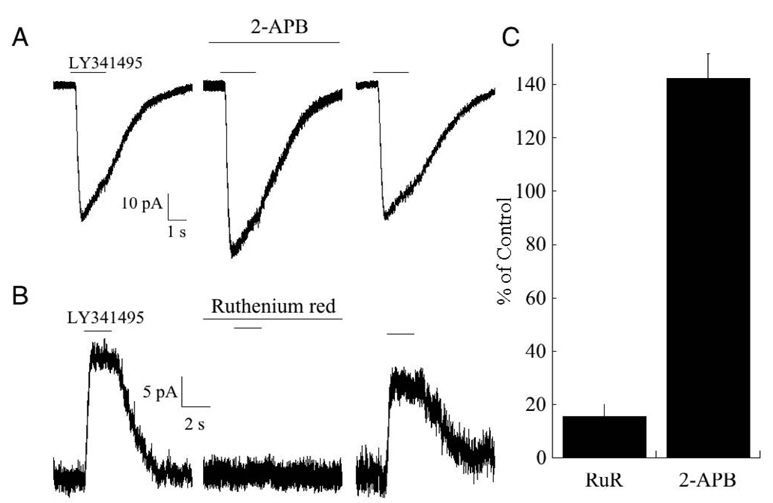
Fig. 2. Pharmacological properties of the cationic transduction channel.
(A) Response of a mouse rod bipolar cell to application of the mGluR6 antagonist LY341495 (100 µM) before, during and after application of 200 µM 2-APB. Holding potential was −40 mV. (B) Response of another cell before, during, and after application of 10 µM ruthenium red. Holding potential was +40 mV, and thus the responses were outward. (C) Summary of the effects of both compounds on the transduction current. Ruthenium red strongly reduced the current (n=8; p<.01, Student’s t test), while 2-APB (200 µM) potentiated the current (n=5; p<.02, Student’s t test).