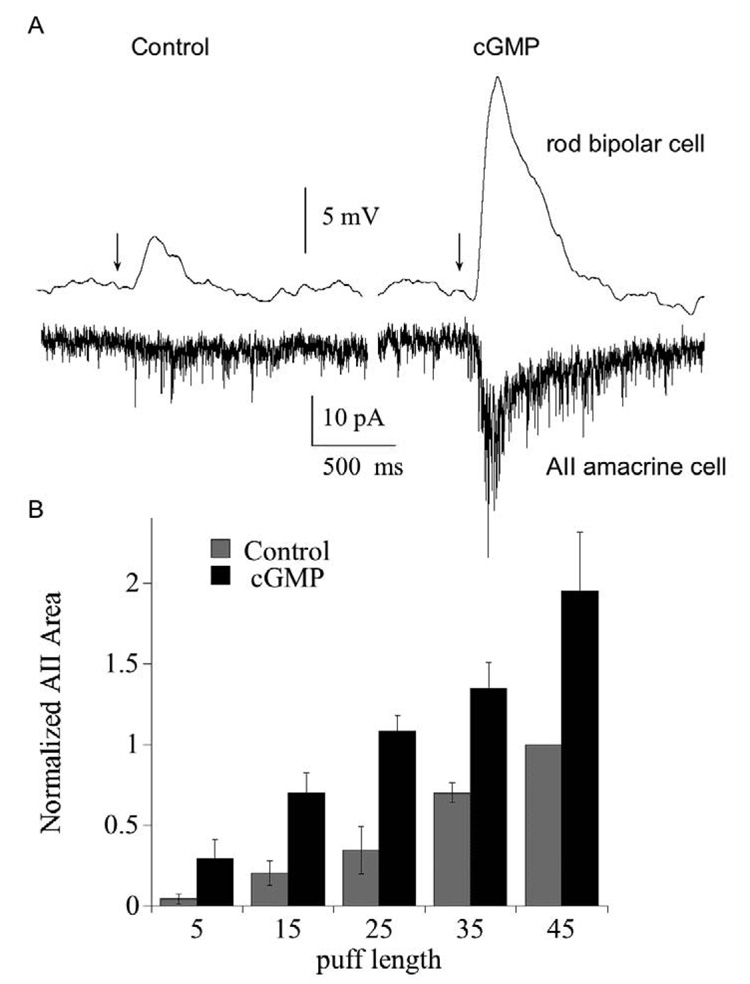
Fig. 5. Potentiation of rod bipolar cell responses is passed forward to the AII amacrine cell.
(A) Paired recordings of a rod bipolar cell (current clamp) and an AII amacrine cell (voltage clamp). Traces on the left show the response of the rod bipolar and amacrine cell to a 15 ms puff of the mGluR6 antagonist CPPG immediately after breaking into the rod bipolar cell. Traces on the right show the responses 10 minutes later. Bipolar cell pipet contained 1 mM cGMP. Bath solution contained 4 µM L-AP4. Each trace is the average of 3 responses. (B) Summary of the effect of rod bipolar cell cGMP on the postsynaptic response of the AII amacrine cell, plotted as a function of puff length. Amacrine cell responses were integrated over the first 500 ms following the CPPG puff, and each was normalized to the current elicited by the 45 ms control puff (i.e., prior to dialysis with cGMP). For each puff, n=6 (15 and 25 ms puff) or 8 cells (5, 35, 45 ms puffs). P<.05 for 15–45 ms puff.