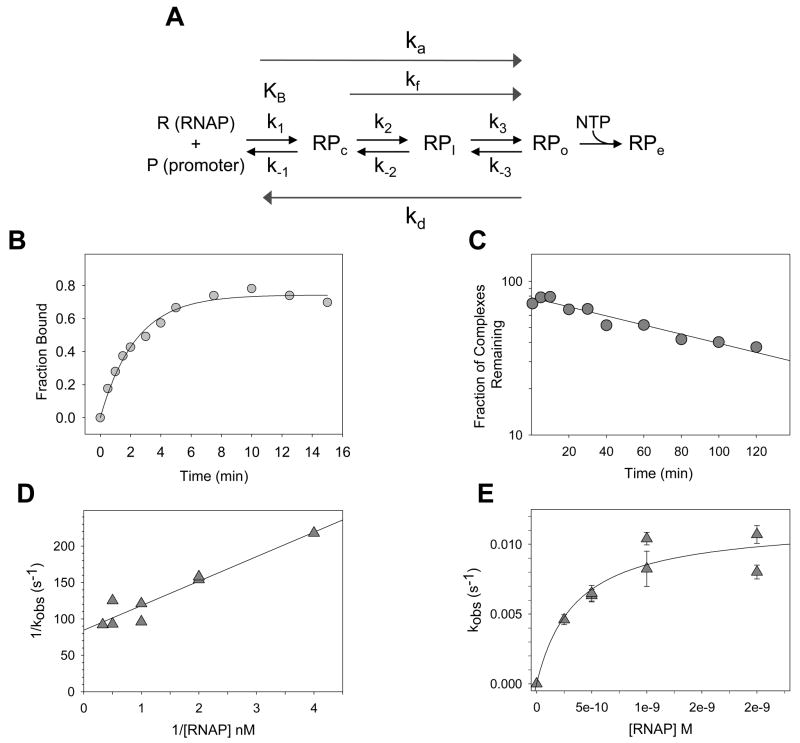
Fig. 5.
Analysis of kinetic parameters of RNAP-promoter complex formation. A) Multiple steps in the process of forming an RNAP-promoter open complex. R: (RNAP); P: promoter DNA; RPc: closed complex, competitor-sensitive; RPI: intermediate complex, DNA strands closed; RPo: open complex, DNA strands open. RPe: elongation complex. NTP: nucleotide substrates. RPo is a competitor (heparin) resistant complex at many, but not all, promoters. KB (or K1): equilibrium constant for formation of RPc; ka: composite second order association rate constant; kf (or ki): RNAP concentration-independent isomerization rate constant (may reflect rates for multiple intermediate steps at some promoters); kd: composite dissociation rate constant. (see [1,2,52]). (B) Time course for formation of a heparin resistant RNAP complex at the lacUV5 promoter. The 32P end-labeled fragment containing the E. coli lacUV5 promoter (−130 to +40) was incubated with 5 nM RNAP at 30°C in buffer containing 110 mM KCl, 10 mM Tris-Cl pH 8.0, 10 mM MgCl2, 1 mM DTT, 100 μg/ml bovine serum albumin (BSA). Aliquots were removed at time intervals, heparin was added (to 10 μg/ml final), and samples were filtered through nitrocellulose filters [86]. The rate constant, kobs, for formation of the complex at this RNAP concentration (7 × 10−3 s−1) was determined from Eq. 1, as described in text. (C) Determination of the dissociation rate of an RNAP-lacUV5 promoter complex. Complexes were formed with a 32P end-labeled lacUV5 promoter fragment (−130 to +40) and 10 nM RNAP at 30°C in the buffer described for panel (B). Competitor (heparin, final concentration 10 μg/ml) was added at t=0, and aliquots were filtered at time intervals. A semi-log plot of complexes remaining as a function of time (in minutes) is shown. The dissociation rate (kd) determined from a single exponential fit of the data was 2.3 × 10−4 (s−1). (D) Tau plot (1/kobs vs 1/[RNAP]) of observed rate constants, kobs, for formation of a heparin resistant RNAP-promoter complex (RPAC) with a 32P end-labeled fragment containing the E. coli rrnB P1 promoter (−88 to +50), determined at a series of RNAP concentrations. Heparin (10 μg/ml) stable complexes at rrnB P1 are formed in the presence of the first two NTP substrates (ATP, CTP), which produces a 5-mer transcript [58,63]. Complexes were formed at 25°C in buffer containing 45 mM NaCl, 10 mM Tris-Cl pH 8.0, 10 mM MgCl2, 1 mM DTT, 100 μg/ml bovine serum albumin (BSA), 500 μM ATP and 50μM CTP. Values for kobs were determined as shown in panel B, using Eq. (1). The overall association rate constant, ka, determined from a fit of the data to Eq. (2), was ~3.0 × 107 M−1 s−1, and kf was 1.2 × 10−2 s−1. (E) Nonlinear plot (kobs vs. [RNAP]) of the same data as in (D). ka, from fit of data to Eq. (3) was 3.3 × 107 M−1 s−1, and kf was 1.2 × 10−2 s−1.