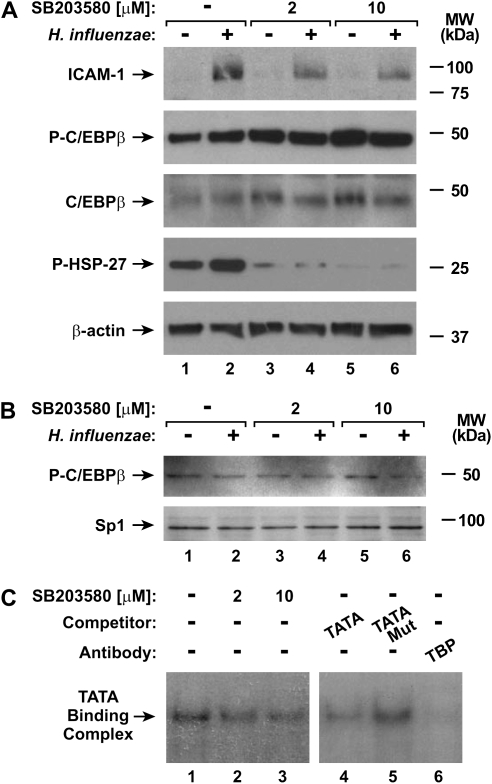
Figure 7.
Inhibiting p38 MAP kinase phosphorylation alters TFIID function. (A) ICAM-1, phosphorylated and total C/EBPβ, HSP27, and β-actin protein levels were assessed using immunoblot analysis of extracts from hTBE cell monolayers that were left untreated or were pretreated with a p38 inhibitor at the indicated concentrations, and then incubated without or with H. influenzae for 24 hours. (B) Phosphorylated C/EBPβ and Sp1 nuclear protein levels were assessed using immunoblot analysis of nuclear protein extracts from hTBE cell monolayers that were left untreated or were pretreated with a p38 inhibitor at the indicated concentrations, and then incubated without or with H. influenzae for 4 hours. (C) Transcription factor binding to a TFIID consensus sequence were assessed using EMSA with nuclear extracts from hTBE cell monolayers that were left untreated or were pretreated with a p38 inhibitor at the indicated concentrations, and then incubated with H. influenzae for 4 hours. Specificity of protein binding was assessed by competition with unlabeled oligonucleotides containing the TFIID consensus sequence (TATA), but not a mutated sequence (TATA Mut). TFIID participation in the binding complex was identified using supershift analysis by addition of antibody against TBP. The position of TATA-binding complexes is indicated by an arrow. Results in all panels are representative of three experiments.