Figure 1.
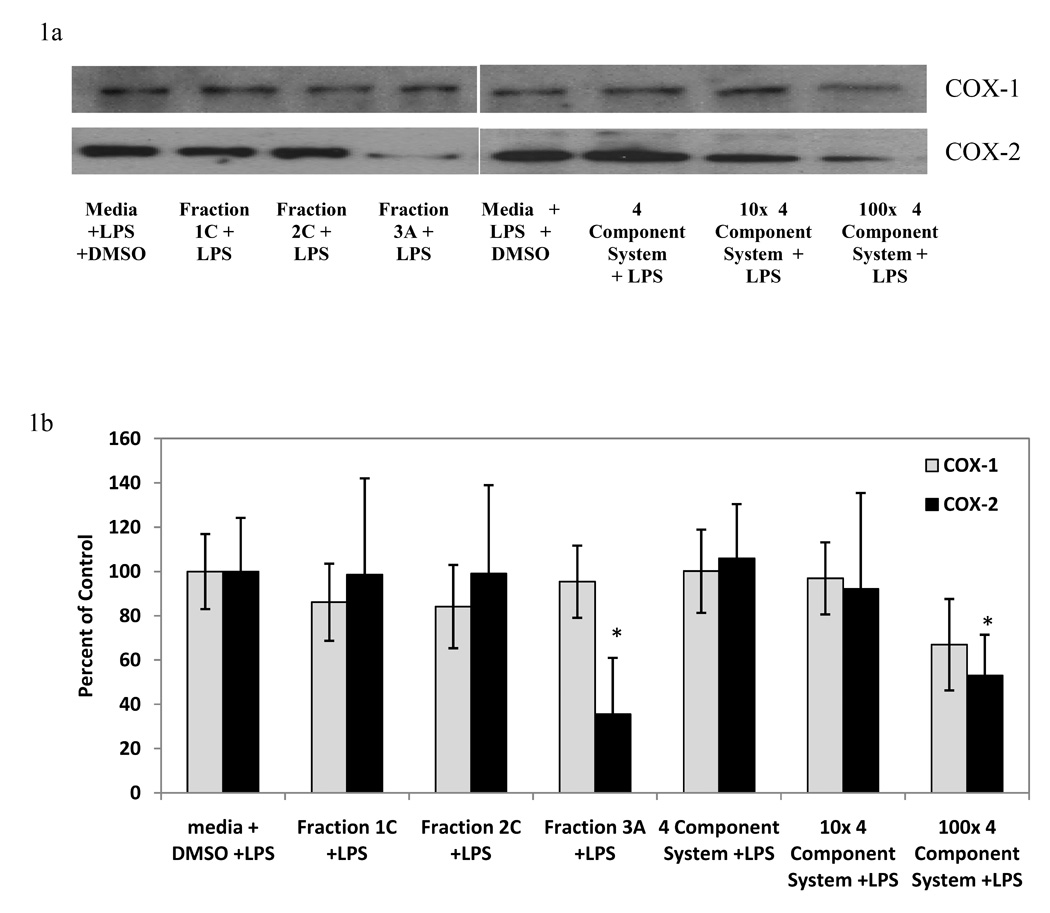
Representative western blots (Figure 1a) and semi-quantitative representation (Figure 1b) of the effect of light-activated Hp fractions (10 µg/ml) and 4 component systems on LPS-induced COX-1 and COX-2 protein levels in RAW 264.7 mouse macrophages. The 4 component system is composed of: 0.07 µM quercetin, 0.08 µM amentoflavone, 0.2 µM chlorogenic acid, 0.03 µM pseudohypericin. Data is represented as mean percent of media + DMSO + LPS control ± standard error. n=4 for each. Treatments without LPS did not significantly affect either COX-1 or COX-2 protein as compared to media + DMSO control (average 98 ± 12% of control). LPS increased the expression of COX-2 protein (29 ± 16 % of control for media + DMSO, 100 ± 17 for media + LPS + DMSO) but not COX-1 protein (100 ± 15 % of control for media + DMSO). Dark treatments did not significantly affect LPS-induced COX-1 or COX-2 protein levels (average 99 ±15% of control). Quercetin (100 µM) used as a positive control for reduction in LPS-induced COX-2 protein (27 ± 22 % of control). Quercetin did not affect LPS-induced COX-1 protein (103 ± 18% of control). * p-value < 0.05 as compared to media + LPS + DMSO control.
