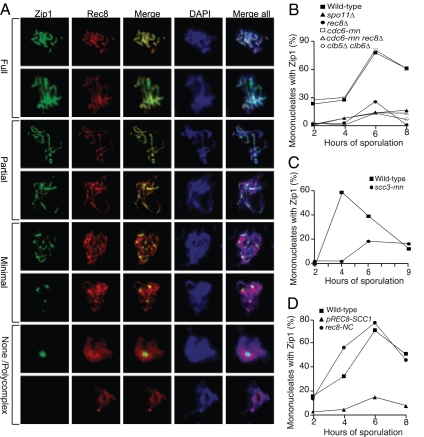
Figure 3.
Meiotic cohesin complexes are required for Zip1 assembly. (A) Examples of meiotic cells that were harvested and assayed for Zip1 staining on chromosome spreads. Cells carry a Rec8-3HA construct. α-Zip1 staining is shown in green, α-HA in red, and DNA in blue. (B) Wild-type (A7097, ■), spo11Δ (A8477, ▴), rec8Δ (A16664, ·), cdc6-mn (A15880, □), cdc6-mn rec8Δ (A17021, ▵), and clb5Δ clb6Δ (A16113, ○) were induced to sporulate. At the indicated times, cells were harvested and chromosome spreads were assayed for Zip1 staining. In this and subsequent experiments, the “percentage of mononucleates with Zip1” encompasses cells with partially and fully assembled Zip1 as defined in A. The percentage of cells in the individual Zip1 categories is shown in Supplemental Figure S4. The meiotic progression of these strains is shown in Supplemental Figure S3A. In this and subsequent experiments 100 mononucleate cells were counted per strain per time point. (C) Wild-type (A1972, ■) and scc3-mn (A20163, ·) were induced to sporulate. At the indicated times, cells were harvested and chromosome spreads were assayed for Zip1 staining. The percentage of cells in the individual Zip1 categories is shown in Supplemental Figure S5. The meiotic progression of these strains is shown in Supplemental Figure S3B. (D) REC8-3HA (A13946, ■), pREC8-SCC1-3HA (A16132, ▴), and REC8-NC (A13539, ·) were induced to sporulate. At the indicated times, cells were harvested and chromosome spreads were assayed for Zip1 staining. The percentage of cells in the individual Zip1 categories is shown in Supplemental Figure S6. The meiotic progression of these strains is shown in Supplemental Figure S3C.