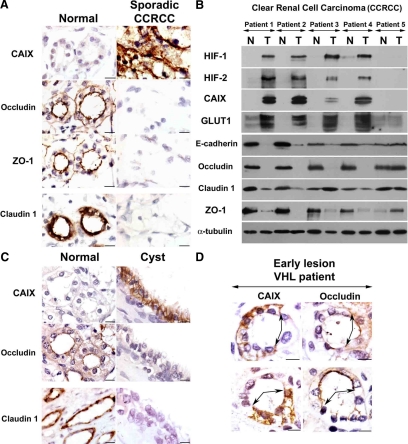
Figure 2.
TJs are disrupted after VHL inactivation in renal-derived cells in vivo. (A) Serial sections from a representative sporadic VHL-defective CCRCC, which also includes adjacent unaffected tissue. Labeling was performed for ZO-1, occludin, claudin 1, and CAIX. Micrographs show representative fields of normal and tumor tissue from different areas of the same section. (B) Western blot with the indicated antibodies of five sporadic VHL-defective CCRCC tumors and paired unaffected kidney tissue. N, normal tissue; T, tumor. Consistent with VHL inactivation in the majority of sporadic CCRCCs, four of five tumors showed HIF activation (patients 1–4). E-cadherin, occludin, and ZO-1 were down-regulated in all four tumors displaying HIF activation; results with claudin 1 were more variable. (C) Serial sections labeled with the indicated antibodies of kidney tissue containing a cyst from a VHL patient (images are presented as in A). Ten independent cysts were analyzed with similar results. (D) Serial sections containing an early lesion of VHL inactivation (in an otherwise normal tubule) labeled for the HIF target gene CAIX and occludin. Early lesions from five VHL patients were analyzed and showed similar results. Bar, 10 μm.