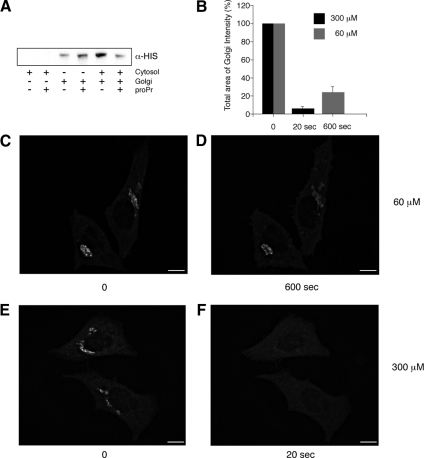
Figure 1.
Inhibition of DAG formation through PAP1 results in a rapid loss of ARFGAP1 from Golgi membranes. (A) Inhibition of ARFGAP1 binding to Golgi membranes by proPr is cytosol-dependent. Recombinant His-tagged ARFGAP1 (0.1 μg) was incubated in 200 μl reaction buffer (see Material and Methods) together with highly purified Golgi membranes (20 μg), rat liver cytosol (1 mg), or proPr (300 μM) for 15 min at 37°C. Incubation mixtures were terminated on ice and membranes pelleted at 13 000 rpm for 10 min. Solubilized proteins were then separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred to nitrocellulose for Western blotting. His-ARFGAP1 was detected using a poly-His specific antibody followed by secondary HRP-labeled rabbit anti-mouse antibody and an ECL detection system. (B–F) Addition of 60 μM proPr for 600 s (C and D) or 300 μM proPr for 20 s in HeLa cells expressing ARFGAP1EGFP (E and F), respectively, results in a partial or complete loss of the Golgi-localized ARFGAP1EGFP. (B) Quantitation (abscissa) as described in Materials and Methods. Scale bars, (C–F) 10 μm.