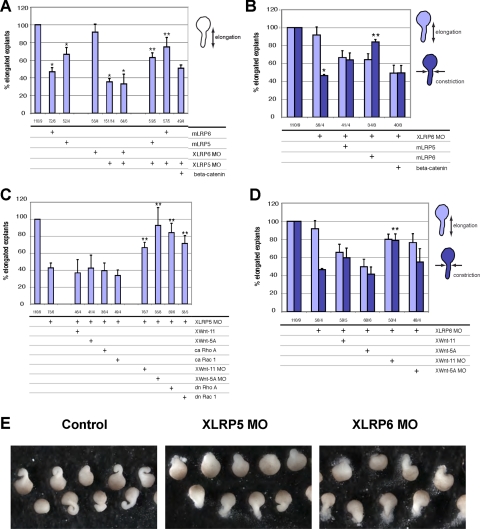
Figure 2.
Lrp5/6 are crucial regulators of convergent extension (CE) movements in Xenopus. (A and B) Injection of Lrp5 or Lrp6 mRNA or XLRP5/6 MOs all inhibit convergent extension of Keller explants from stage 10.5 that are rescued by mLrp5/6 but cannot be rescued by β-catenin coinjection (*, significant difference from control; **, significant rescue of MO, p > 0.95). (C and D) The CE defects induced by XLRP5 MO or XLRP6 MO are not rescued by Wnt5a or Wnt11 overexpression or constitutively active (ca) RhoA and Rac1. However, down-regulation of noncanonical signaling by XWnt5a or XWnt11 MO rescued XLRP5 and XLRP6 depletion phenotypes. XLRP5 MO induced inhibition of elongation was also rescued by dn RhoA and Rac1 (**, significant rescue of MO; p > 0.95). (E) Typical morphology of Keller explants injected with XLRP5 and XLRP6 MOs. The numbers under the graphs indicate number of injected embryos/number of independent experiments.