Figure 2.
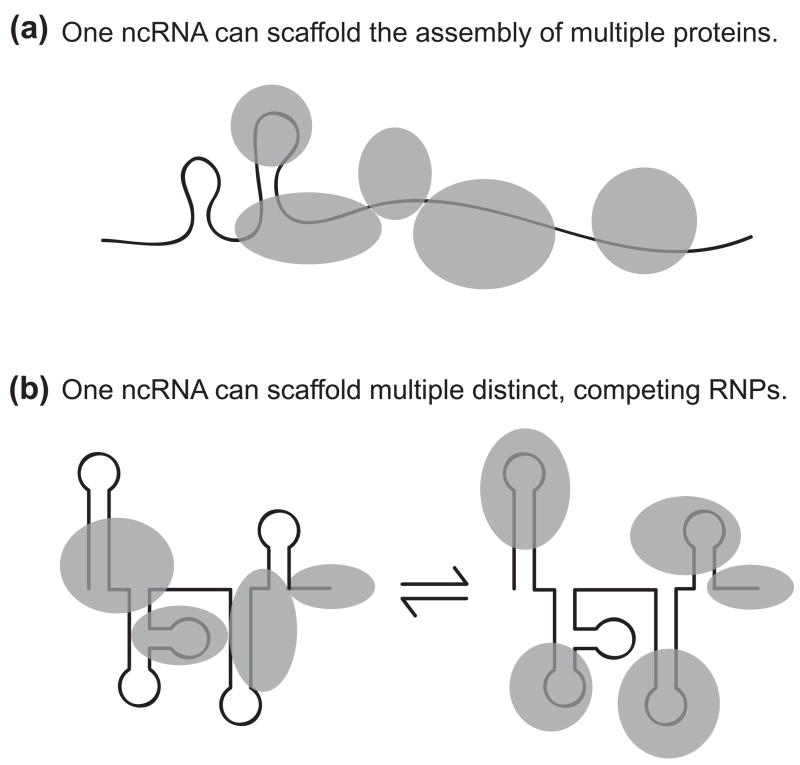
Non-coding RNA function as a scaffold of macromolecular assembly. The ability of even small RNA motifs (of less than 20 nucleotides) to fold uniquely and with high thermodynamic stability is one of several features that suggest ncRNA would be well suited to serve as a versatile scaffold of macromolecular assembly. Gain of RNP scaffold complexity can occur by increasing the number of proteins in a single macromolecular assembly, for example by recruiting additional proteins to join the complex, and/or by alternative assembly of distinct RNPs on a single ncRNA. (A) A long ncRNA can recruit multiple proteins that are independent or cooperative in their RNP assembly. Multimerization of the ncRNP is possible as well, either by RNA-RNA or protein interactions. In the case of the Drosophila roX RNAs, in addition to providing a scaffold, ncRNA motifs regulate the activity of bound proteins. (B) A single ncRNA can assemble distinct RNPs. In the case of human 7SK RNA, some RNP components are mutually exclusive in their ncRNA association. Distinct 7SK RNPs assemble and disassemble in a dynamic, stress-regulated equilibrium.