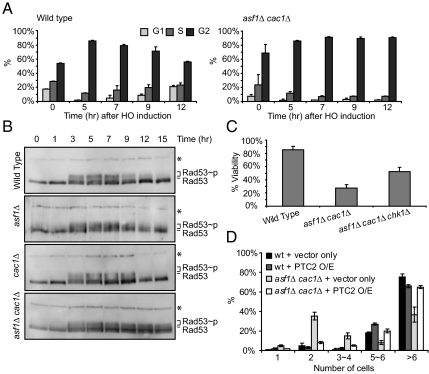
Fig. 2.
asf1Δcac1Δ cells are deficient in recovering from the DNA damage checkpoint-mediated arrest. (A) Wild-type and asf1Δ cac1Δ MATα cells lacking HML and HMR were grown in YEP/Lactate medium to the exponential phase and then 2% galactose was added to induce HO endonuclease. Cells were observed microscopically. Unbudded cells (G1), small budded cells (S), and large budded cells (G2/M) were counted. Three different experiments counting 100–200 cells were performed to obtain the average shown in this figure. Error bars indicate SDs. (B) Western analysis with anti-Rad53 antibody determined the extent of phosphorylated Rad53 in whole cell extracts of wild-type and mutant cells during DSB repair. Phosphorylated Rad53 (Rad53∼p) migrates slowly compared to unphosphorylated Rad53 (Rad53). * indicates a nonspecific band detected by cross-reactivity of the Rad53 antibody, which was used as a loading control. (C) Percent viabilities were measured as described in Fig. 1. (D) Wild-type (YJK17) and its derivatives lacking Asf1 and/or Cac1 were grown in YEP/Lactate media to the exponential phase and then the unbudded cells (G1) were micromanipulated on galactose plates. Overexpression (O/E) of Ptc2 was driven by galactose-inducible promoter. One day after plating, the number of cells derived from a single cell was counted under the microscope. The graph shows the average of 3 different experiments with error bars representing SDs.