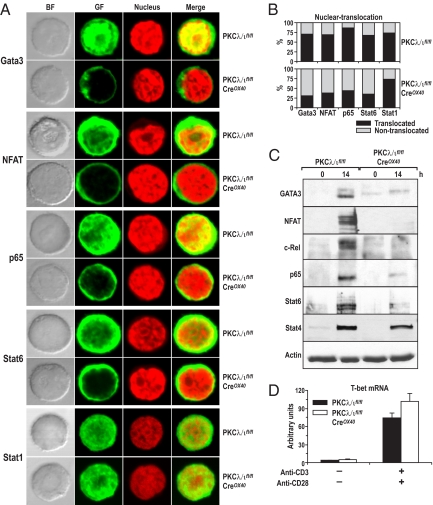
Fig. 5.
Deletion of PKCλ/ι in vivo in activated T cells regulates Th2-transcription factors. (A) Purified naïve splenic CD4+ T cells were activated with anti-CD3/CD28 for 14 hours. Cells were harvested and adhered onto polyY-L-lysine–coated coverslips for immunofluorescence staining. Nuclei were stained by propidium iodide. Cells were analyzed by using a confocal microscope. Nuclear translocation of Th2 transcription factors is shown. Images are representative examples from > 300 cells for each staining and are taken from a single experiment that is representative of 3 independent experiments. (B) Cells with nuclear translocation were quantified by cell counting (n > 400) under microscope. T cells were pooled from 7 mice per genotype. (C) Nuclear extracts of T cells treated as above were analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies for the respective transcription factors. (D) T-bet mRNA levels are shown (arbitrary units). Total RNA was extracted from splenic CD4+ T cells stimulated with anti-CD3/CD28 for 14 hours for real-time PCR analysis. All samples were determined by triplicate; the data are normalized to an 18S reference. BF, bright field; GF, green fluorescence.