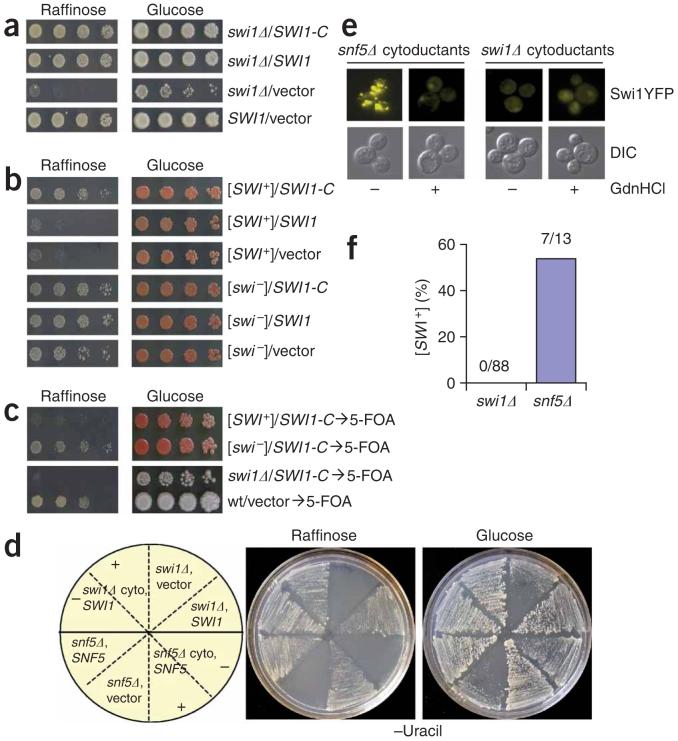
Figure 6.
Swi1 is the protein determinant of [SWI+]. (a) The C domain is sufficient for Swi1 function. Shown are S288C swi1Δ cells containing p416TEFSWI1-C (SWI1-C), p416TEFSWI1 (SWI1) or p416TEF (vector). Wild-type S288C with p416TEF was included as a control. (b) SWI1-C, but not the full-length SWI1, was able to ‘complement’ the Raf- phenotype of [SWI+]. Cells of 74D-694 [PSI+][SWI+] and [PSI+][swi-] containing p416TEFSWI-C (SWI1-C), p416TEFSWI1 (SWI1) or p416TEF (vector) were examined for growth on the indicated plates. (c) Swi1-C was able to phenotypically ‘mask’ but not cure [SWI+]. After plasmid removal, [SWI+] and swi1Δ cells were re-assayed as described in a and b. (d) Swi1 is required for [SWI+] propagation. [SWI+] was cytoduced to isogenic swi1Δ and snf5Δ cells, and the resulting cytoductants were transformed with a SWI1 expression plasmid for swi1Δ cells (swi1Δ cyto, SWI1) or SNF5 for snf5Δ cells (snf5Δ cyto, SNF5). Isogenic swi1Δ and snf5Δ cells were also included as controls. Cell streaks of each representative transformant before (-) or after (+) 5 mM guanidine hydrochloride treatment are shown on the indicated plates. (e) Swi1-YFP is aggregated in the snf5Δ but not in the swi1Δ cytoductants after [SWI+] cytoduction. Cytoductants of swi1Δ and snf5Δ were treated with (+) or without (-) 5 mM guanidine hydrochloride followed by transformation of p416TEF-SWI1YFP and analysis by fluorescence microscopy. (f) Summary of the [SWI+] cytoduction experiments. Shown are the results of three independent experiments.