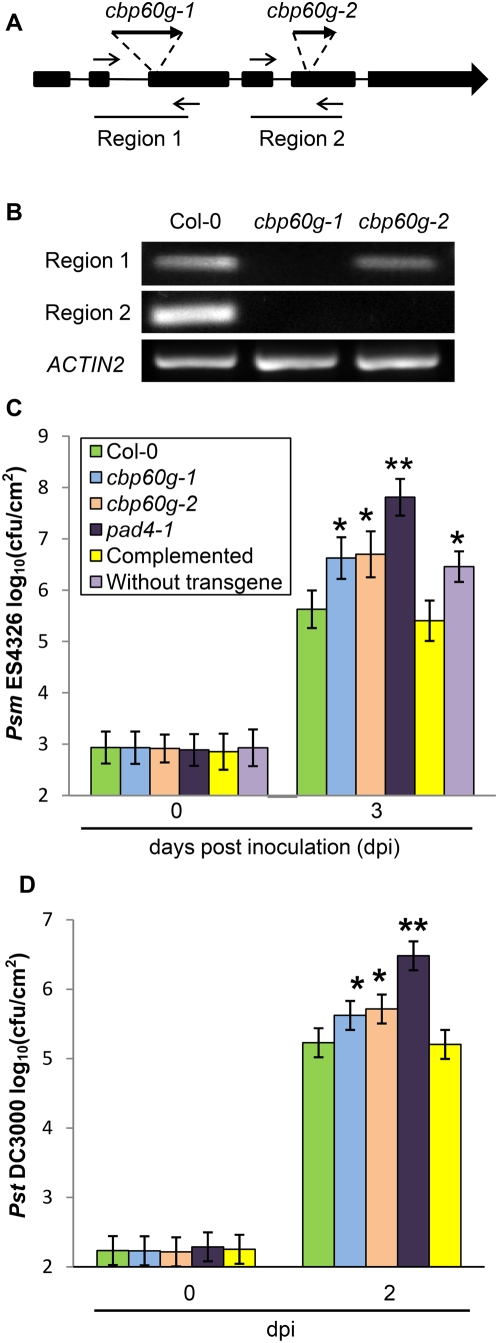
Figure 2. Mutants of CBP60g support more bacterial growth than wild-type plants.
(A) Illustration of CBP60g mutants cbp60g-1 and cpb60g-2. Bold lines, exons; thin lines, introns; bold arrows: T-DNA insertions; thin arrows, primers used for RT-PCR. (B) RT-PCR results showing two regions of the CBP60g transcript. (C) Bacterial growth assays using Psm ES4326. Each bar at 0 hours or 72 hours represents data from 4 or at least 16 replicates, respectively. Error bars represent standard deviation from 16 samples. Asterisks, p<0.05. P values were calculated using the two-tailed Mann-Whitney U-test. Similar results for the cbp60g mutants were obtained in two other independent experiments. Complemented, cbp60g-1 plants carrying wild-type CBP60g as a transgene; Without transgene; siblings of the complemented plants lacking the transgene.