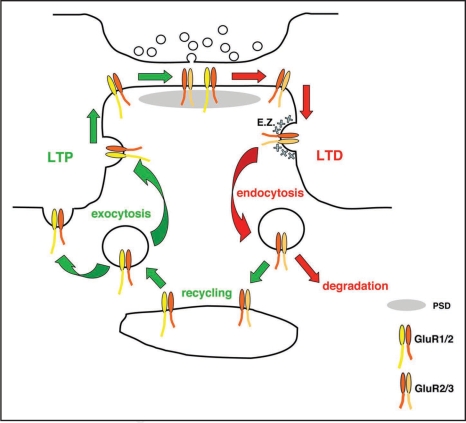
Figure 1.
AMPA receptor trafficking pathways during synaptic plasticity. Long-term potentiation involves the exocytosis of GluR1-containing AMPARs, that originate from recycling endosomes, at sites either on the dendritic spine or shaft. They subsequently drift laterally in the plane of the plasma membrane to reach the postsynaptic density. Long-term depression involves the lateral movement of GluR2-containing AMPARs from the PSD to designated endocytic zones (E.Z.) on the dendritic spine. Following internalization by clathrin-mediated endocytosis, AMPARs are sorted to lysosomes for degradation. During constitutive trafficking, AMPARs are internalized from E.Z.s, and traffic via recycling endosomes back to the plasma membrane.