Figure 7. SPON-1 maintains process position at the ventral midline.
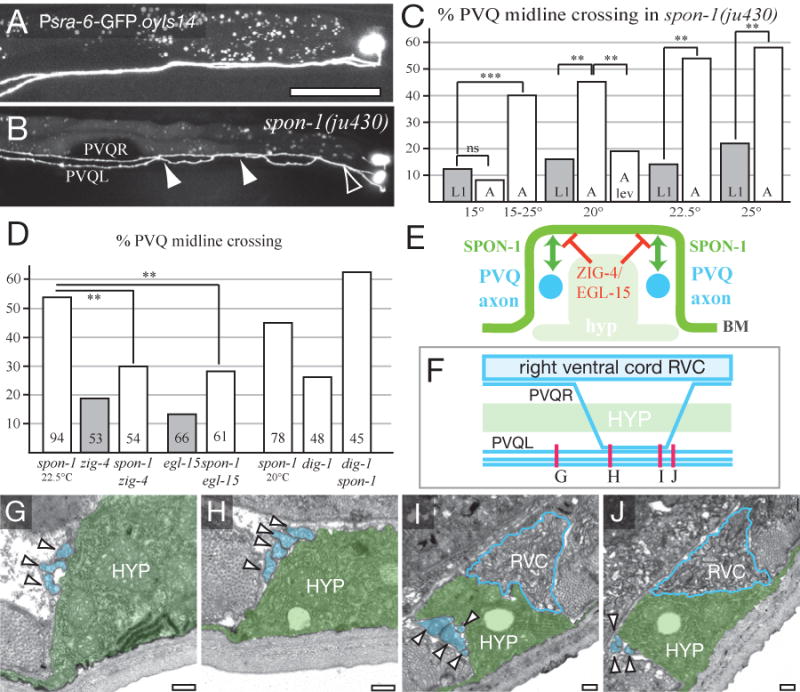
(A) PVQ axons in wild type (oyIs14). (B) In spon-1(ju430) PVQL crosses over to the right-hand VNC (open arrowhead) as in the wild type, and undergoes two ectopic crossovers (filled arrowheads). (C) Midline crossing is more penetrant in spon-1 adults than in L1s, is enhanced by shifting L1s from 15 to 25°C, and suppressed by growth in 1 mM levamisole (see Table S1). (D) Suppression of spon-1(ju430) midline crossing by zig-4 and egl-15 (at 22.5°C; number of animals shown in column) and enhancement by dig-1 (at 20°C). (E) Model for the interaction of SPON-1 and ZIG-4/EGL-15A pathways; cross-section of ventral nerve cord. SPON-1 in the BM (green) mediates adhesion of PVQ axons (blue) to their normal environment; ZIG-4 and EGL-15 (red) locally inhibit axon-BM adhesion at the midline. (F-J) spon-1(ju430ts) oyIs14 animals were shifted from 15°C to 25°C in the L1 stage and PVQ scored in young adults. The adults were sectioned in the region of PVQ crossing over posterior to the vulva; approximate levels of sections are shown in F. (G) Anterior to PVQR crossover (0 μm) the left-hand ventral nerve cord contains its normal three processes, PVQL, PVPR and AVKR (arrowheads and colored blue in G-J). (H,I) Between 90 and 150 μm a fourth process, presumably PVQR, has crossed over and fasciculated with the left hand bundle. (J) At ∼160 μm posterior the left hand bundle now again contains three processes. The ventral hypodermal ridge (HYP, green) and the right-hand ventral nerve cord (RVC, blue outline) appear normal in both crossover regions. Similar results were obtained for a second animal (not shown). Scale, 0.2 μm (G-J).
