Figure 1.
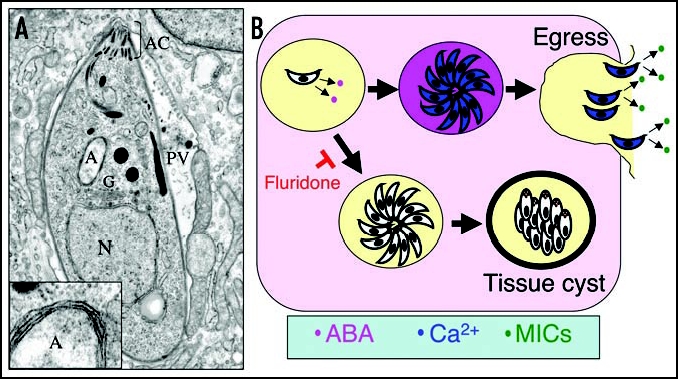
ABA production in T. gondii. (A) Cross-section through an intracellular T. gondii showing organellar structures. Insert illustrates four surrounding membranes from enlarged apicoplast. N, nucleus; A, apicoplast; AC, apical complex consisting of conoid and secretory organelles; PV, parasitophorous vacuole. (B) Model of ABA production by the parasite with in the PV. Accumulation of ABA (pink) leads to increases in intracellular calcium (blue) activating egress and triggering secretion of micronemes (MICs shown in green). Fluridone blocks ABA production, preventing egress and favoring differentiation of tissue cysts.
