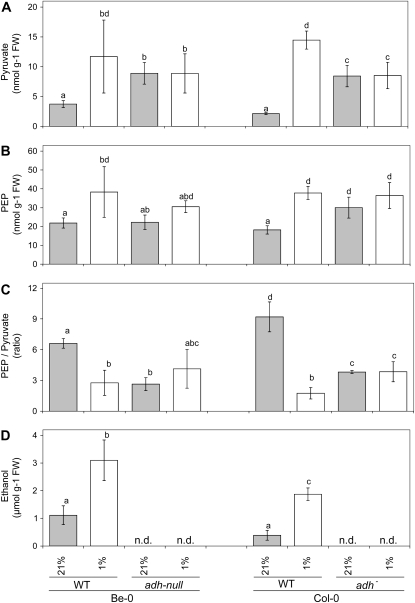
Figure 7.
The impact of ADH activity in 3-week-old Arabidopsis seedlings on the levels of pyruvate (A), PEP (B), and the ratio PEP to pyruvate (B) was tested under ambient air conditions (21% [v/v] oxygen in the air; gray bars) or after 24 h of a near-anoxic treatment with air containing 1% (v/v) oxygen (white bars). The seedlings used for these analyses were growing on sterile horizontal agar-plates. The levels of pyruvate and PEP were measured in plants of the wild-type (WT) Arabidopsis accessions Be-0 and Col-0 and compared with the values measured in two independent adh mutants (adh-null in the background of Be-0, and adh− in the Col-0 background). In a parallel experiment, ethanol production by the two wild-type accessions was determined (D) by measuring ethanol leakage into liquid incubation medium surrounding the seedlings, which was either aerated with ambient air, or with air containing 1% (v/v) oxygen. Multiple comparison analysis by the Holm-Sidak test following a two-way ANOVA indicated the oxygen-induced differences between the levels of pyruvate, PEP, and the PEP-to-pyruvate ratio in wild-type plants as significant (P < 0.05). Within knockout lines, all values measured were not statistically different from each other (P < 0.05). Bars represent the mean of at least three measurements ± se. Bars marked with the same letter do not differ significantly from each other. n.d., Not determined.