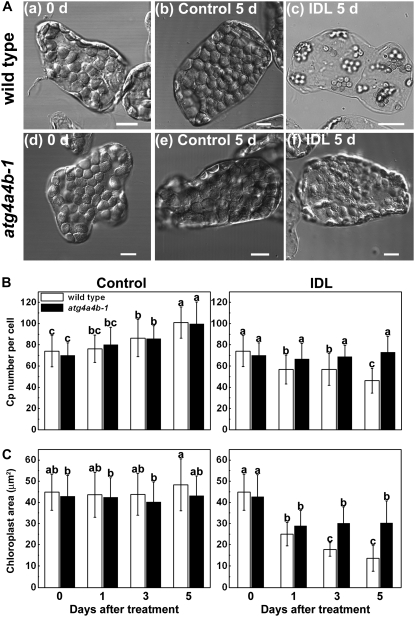
Figure 4.
Visible chloroplast catabolism proceeds in IDLs of wild-type plants, but is suppressed in those of atg4a4b-1. A, Differential interference contrast images of chloroplasts in mesophyll cells separated from leaves of wild-type (a) and atg4a4b-1 (d) plants before the treatment, from control leaves of wild-type (b) and atg4a4b-1 (e) plants after the 5-d treatment, and from IDLs of wild-type (c) and atg4a4b-1 (f) plants after the 5-d treatment. Leaves were cut into small pieces, fixed with 3.5% glutaraldehyde, and mesophyll cells were individually dispersed on the glass plate and observed by microscopy. Bars = 10 μm. B and C, Changes in the number (B) and the area (C) of chloroplasts in control leaves and IDLs of wild-type (white columns) and atg4a4b-1 (black columns) plants during the treatment. Chloroplasts in mesophyll cells were identified by those exhibiting chlorophyll autofluorescence during LSCM. The number of chloroplasts per cell and their length and breadth were counted on differential interference contrast images (shown as A) of mesophyll cells separated from leaves. Chloroplast area was calculated using the assumption that chloroplasts were ovals. Data are means ± sd (n = 50 in the no. per cell; n = 45 in the area). Statistical analysis was performed by Tukey-Kramer's HSD test. Different letters in each graph denote differences at P ≤ 0.01.